Global personal wealth has become a focal point of discussion in recent years, reflecting significant disparities in wealth distribution around the world. The latest reports indicate that the US and China alone claim over half of this wealth, accounting for 54% combined, while Europe lags behind with just 22%—a stark contrast mainly driven by its five largest economies. According to the Global Wealth Report 2025, understanding the intricacies of personal wealth by country reveals much about economic trends and inequalities today. The data highlights how wealth concentration affects not only individual nations but also the broader dynamics of global economies. As we delve deeper into the topic of wealth distribution, we uncover the factors that contribute to these disparities and their implications for future economic stability.
The examination of global financial resources sheds light on the varying levels of opulence and economic health experienced across different regions and nations. As we navigate through terms like financial wealth and asset distribution, it’s crucial to recognize how the richest countries dominate economic landscapes. The staggering facts within the global wealth landscape reveal not only where most affluence is concentrated but also the emerging trends impacting wealth across European economies and beyond. The contrast in wealth accumulation between major powers shapes not just economic policies but also social structures, making this topic more than just a matter of numbers. Exploring these dynamics allows us to better understand the global wealth report and the intricate tapestry of personal fortunes shaping our world.
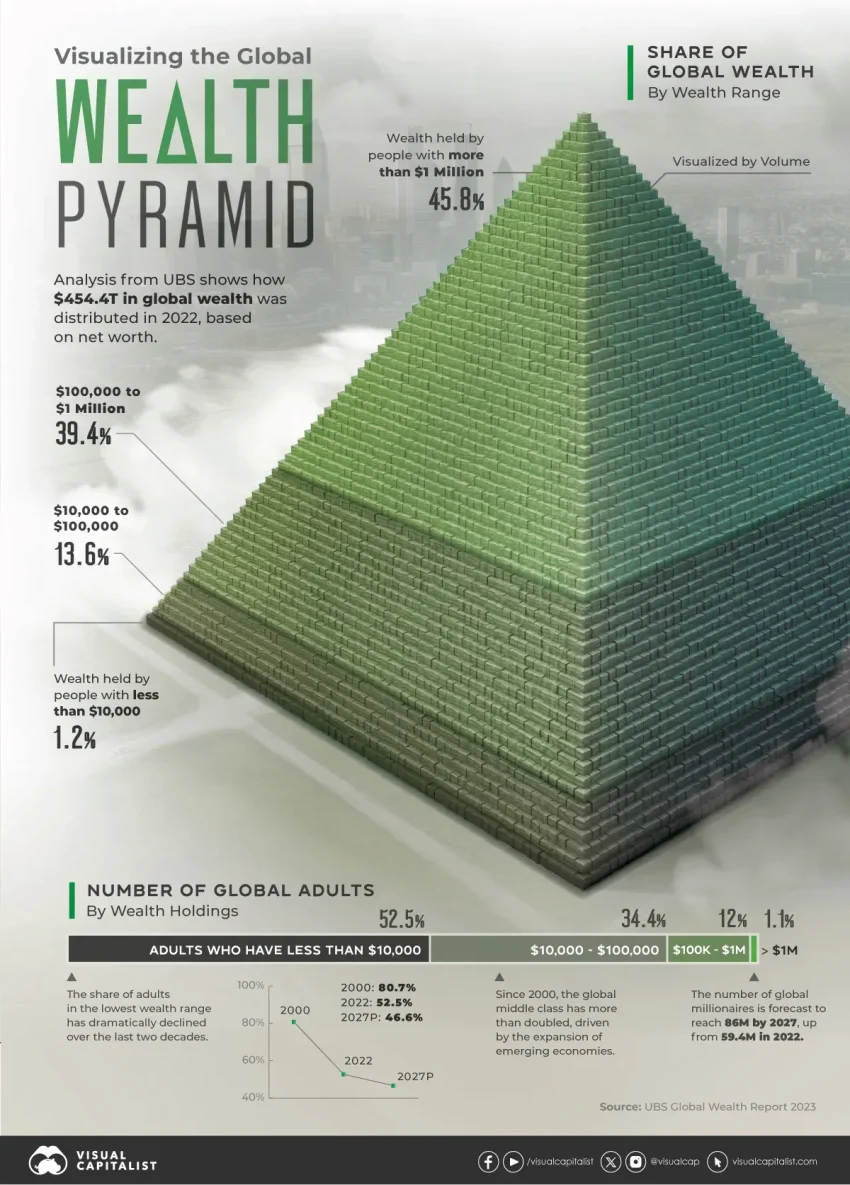
Global Personal Wealth Distribution
The distribution of global personal wealth is characterized by significant imbalances, with the US and China holding a staggering 54% of the world’s assets. This disproportionate share highlights the economic dynamics between these two nations, particularly given their large populations and developed financial systems. As noted, the US alone accounts for approximately 34.7% of global wealth, underscoring its status as a leading economic power. In a broader context, the distribution patterns indicate that wealth is not shared equally across nations, creating a landscape of both abundance and scarcity globally.
In contrast, European nations collectively hold 22.3% of global wealth, which, while substantial, shows a significant gap compared to the shares held by the US and China. The findings in the recent UBS Global Wealth Report 2025 suggest that the wealth concentration within Europe is largely attributed to a few key economies—specifically, the UK, Germany, and France. While Eastern Europe’s wealth is on the rise, the stark differences in wealth distribution highlight the urgency for policies aimed at promoting equity and addressing wealth inequality within and across these regions.
The Rise of Wealth in Eastern Europe
Interestingly, Eastern Europe has emerged as a growth engine for personal wealth, with an impressive increase of over 12% from 2023 to 2024. This rapid growth is notable, especially when compared to the stagnant or declining wealth levels in many Western European countries. The emergence of new millionaires within this region underscores a transformative economic shift, one that could redefine the traditional wealth dynamics observed in Europe. Nations within Eastern Europe are beginning to attract investments and cultivate entrepreneurial endeavors, contributing to this newfound prosperity.
The growth in personal wealth also reflects broader economic trends, including improvements in GDP and shifts in labor markets. As Eastern European countries develop stronger economic infrastructures and financial systems, they are likely to continue their upward trajectory. However, while this growth presents opportunities, it also introduces challenges related to wealth stratification and social equity. With a growing number of wealthy individuals, policymakers must consider strategies to ensure that this wealth is harnessed for broader societal benefits, rather than deepening existing inequalities.
Wealth Inequality in European Economies
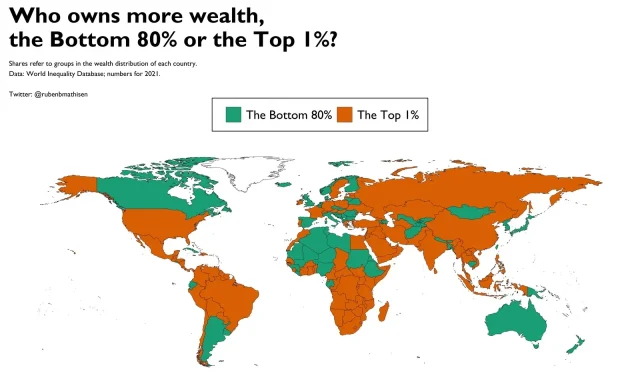
Wealth inequality remains a pressing concern in European economies, particularly as the richest 10% hold a staggering 57.3% of total net household wealth in the eurozone. This concentration of wealth raises questions about economic fairness and access to opportunities for the broader population. While high levels of personal wealth can drive economic growth, the disparity in wealth distribution could perpetuate socio-economic divides, making it difficult for lower-income groups to improve their financial standing.
As the global wealth landscape evolves, it is essential for Eurozone governments to implement policies that promote more equitable wealth distribution. This could involve increasing support for social welfare programs, investing in education and job training, and incentivizing small business growth. By addressing wealth inequality, European economies can create a more inclusive environment that supports sustainable growth, ensuring that the benefits of increased wealth are felt by all.
Impacts of GDP on Global Personal Wealth
There is a strong correlation between a country’s gross domestic product (GDP) and its share of global personal wealth. Countries with higher GDPs tend to accumulate more personal wealth, as evident in the leading economies of the US, China, and several key European nations. The US, for instance, benefits from advanced financial services, innovative technologies, and substantial domestic markets, which all contribute to its high GDP and a corresponding proportion of global wealth.
Conversely, countries with weaker GDP figures often struggle to attract investments and generate personal wealth for their citizens. This correlation highlights the importance of economic policies focused on promoting growth and improving productivity. Enhancing GDP and economic resilience can lead to increased personal wealth among a nation’s population, promoting a more prosperous and balanced global economy.
Comparative Wealth: US, China, and Europe
The comparative analysis of wealth among the US, China, and Europe reveals significant disparities in economic power and personal wealth accumulation. As of 2024, the US leads with a personal wealth share of 34.7%, followed closely by China at 19.4%. These figures starkly contrast with Europe’s share, which, even when including its largest economies, only totals 22.3%. This comparison illustrates not only the economic might of the US and China but also underscores the challenges facing European nations in keeping pace with these economic giants.
This unequal distribution of wealth has historical roots in differing economic systems and stages of development. The US and China’s rapid economic growth, especially in recent decades, has positioned them as leaders in global personal wealth, while Europe’s diverse economies often face constraints that can hinder collective growth. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for Europe to enhance its share of global wealth and ensure that its economies remain competitive in a rapidly evolving global landscape.
The Role of Major European Economies
Major European economies, such as the UK, Germany, and France, play a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s wealth profile. Collectively, these countries account for a substantial portion of Europe’s wealth, with each maintaining significant shares that contribute to the broader economic landscape. For instance, the UK leads with a share of 3.84%, followed closely by Germany at 3.76%. This concentration of wealth among major economies provides a stabilizing effect for Europe but also highlights the dependency on these nations for economic growth.
However, the dominance of these economies can also create a risk for the overall financial health of Europe. If any of these countries experience economic downturns, it could have ripple effects throughout the continent, underscoring the need for diversification and economic innovation. Strengthening ties among all European nations, including supporting smaller economies, could cultivate a more resilient economic structure and promote a balanced approach to wealth distribution across the region.
Wealth Growth Trends in Greater China
Greater China, encompassing mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan, has experienced notable growth in personal wealth, expanding by 3.4% from 2023 to 2024. This increase demonstrates the sustained economic momentum in the region, driven by robust manufacturing, technological advancement, and a growing consumer base. As more individuals gain wealth, Greater China solidifies its position as a significant player in the global wealth arena, contributing to nearly 20% of personal wealth worldwide.
The wealth generated in Greater China not only impacts the region’s economic standing but also influences global trends in investment and consumption. Chinese consumers are increasingly recognized for their buying power, and changes in their spending habits can reverberate across global markets. Understanding the trends in personal wealth within this region is essential for businesses and investors looking to capitalize on future growth opportunities, as Greater China continues to thrive in the global economy.
Future Projections for Global Wealth
As we look towards the future, projections for global wealth indicate a trend of gradual increase, albeit with notable regional variations. The wealth accumulation trend is expected to continue, albeit at a slower pace compared to the past few years. Analysts forecast that the growing economies in regions like South Asia and parts of Africa may begin to shift the wealth landscape, challenging the current dominance of Western economies.
The Global Wealth Report 2025 serves as a critical resource for understanding these shifts, providing comprehensive insights into wealth distribution across diverse markets. As economic conditions change, it is crucial for stakeholders to remain agile in adapting to these trends. Continuous monitoring of regional wealth variation will be vital for developing strategies that promote inclusive growth and address the pressing issue of wealth inequality on a global scale.
Personal Wealth and Its Definition
Personal wealth is defined as the net worth of individuals, calculated by the total value of their financial and real assets minus any liabilities. This measure offers insight into an individual’s financial health and economic power. Beyond mere numbers, personal wealth reflects the opportunities and resources available to individuals, affecting their standard of living and quality of life.
Understanding what constitutes personal wealth is essential, particularly when analyzing economic disparities across different nations. As wealth expands, the focus must not solely remain on total figures but also on the distribution of wealth among individuals. This comprehensive examination can help identify the underlying causes of wealth inequalities and inform policies aimed at fostering economic fairness across populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of global personal wealth distribution between major economies?
As of 2025, global personal wealth distribution is heavily skewed, with the United States and China controlling over 54% of the world’s personal wealth. Specifically, the US holds approximately 34.7% and China 19.4%, while Europe’s total share is only 22.3%, largely from its five main economies.
How does the US-China wealth comparison highlight global personal wealth trends?
The wealth comparison between the US and China elucidates significant global personal wealth trends, showing that these two countries alone account for over half of global wealth. This reflects their high wealth per adult and substantial populations, contrasting sharply with Europe’s smaller share of personal wealth.
What does the Global Wealth Report 2025 reveal about European economies and personal wealth?
According to the Global Wealth Report 2025, the European economies combined hold only 22.3% of global personal wealth, with the UK, Germany, and France being the largest contributors. This underlines the dominance of the US and China in the global wealth landscape, raising questions about economic growth and wealth distribution in Europe.
Which European countries hold the largest shares of global personal wealth?
In Europe, the UK leads with the highest share of global personal wealth at 3.84%, followed closely by Germany at 3.76% and France at 3.3%. Italy and Spain follow, bringing the top five economies in Europe to a combined share of 15.1%, which still trails behind China’s wealth share.
What impact does GDP have on the distribution of global personal wealth?
GDP significantly impacts the distribution of global personal wealth, generally showing that countries with higher GDPs retain larger shares of total wealth. This is evident in the top five European economies, which collectively account for a notable portion of Europe’s wealth despite being overshadowed by US and China’s wealth figures.
How does wealth inequality affect overall personal wealth in Europe?
Wealth inequality in Europe greatly influences overall personal wealth, with the richest 10% in the eurozone possessing 57.3% of total net household wealth in late 2024. This disparity highlights the uneven distribution of wealth across different demographics within Europe.
What constitutes personal wealth according to the Global Wealth Report?
Personal wealth, as defined by the Global Wealth Report, is the total value of an individual’s financial and real assets, minus any liabilities. This includes private pension fund assets but excludes state pension entitlements, providing a clearer picture of individual wealth across global frameworks.
What trends are emerging in global personal wealth growth across regions?
In recent years, global personal wealth growth has been uneven, with Eastern Europe experiencing the highest increase, over 12% from 2023 to 2024. In contrast, Western Europe saw a decline, highlighting shifting dynamics in global personal wealth trends and the varying economic conditions across different regions.
| Region | Percentage of Global Personal Wealth | Major Countries | Total Personal Wealth (in trillion €) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Total | 100% | – | 471 trillion € |
| United States | 34.7% | – | 150.9 trillion € |
| China | 19.4% | – | 84.2 trillion € |
| Japan | 4.5% | – | 19.7 trillion € |
| Europe (total) | 22.3% | UK, Germany, France, Italy, Spain | 97.4 trillion € |
| UK | 3.84% | – | 16.7 trillion € |
| Germany | 3.76% | – | 16.4 trillion € |
| France | 3.3% | – | 14.3 trillion € |
| Italy | 2.25% | – | 10 trillion € |
| Spain | 1.95% | – | 8.4 trillion € |
Summary
Global personal wealth is increasingly concentrated in the hands of a few major economies, specifically the US and China, which together account for over half of the total wealth worldwide. With significant disparities in wealth distribution, understanding the dynamics of global personal wealth is crucial for comprehending the economic landscape and potential future developments.
#GlobalWealth #USEconomy #ChinaEconomy #FinanceInsights #WealthReport