Wage inequality in Australia has become an urgent issue that demands attention. Despite being considered a lucky country with high living standards, the reality of economic disparity is starkly different. A recent report highlights how many Australians underestimate the prevalence of income inequality, particularly the staggering gender pay gap that continues to persist. With CEOs earning an astronomical 103 times more than the average worker, these disparities reflect deeply entrenched social injustices in our society. To build a more equitable future, it is essential to address the structural issues that fuel this troubling phenomenon.
The uneven distribution of income and economic resources in Australia paints a troubling picture of inequality that extends beyond wages alone. This phenomenon, often referred to as economic disparity, reveals stark contrasts in the financial wellbeing of different demographic groups, especially between genders. With ongoing discussions about the gender pay gap and the disparity between CEO compensation and average worker salaries, it becomes increasingly clear that achieving social justice requires a multi-faceted approach. Australia’s perception of achievement and fairness stands in stark contrast to the harsh realities faced by many, underscoring the need for actionable change. Addressing these disparities will require commitment and collaboration across all sectors of society to fashion an equitable economy.
Understanding Wage Inequality in Australia
Wage inequality in Australia has reached alarming levels, as evidenced by a recent report highlighting the stark gap between earnings across different demographics. The insights reveal not only a disparity in paychecks but also a significant misunderstanding among Australians regarding the actual income distribution in their country. Many Australians overestimate their peers’ financial success, leading to a distorted perception of what it means to achieve a good salary within the country. Instead of focusing on the reality that the wealth generated is concentrated among a small elite, public discourse often remains fixated on the idea that everyone is relatively well-off.
Additionally, the survey findings show that CEO pay has become disproportionately large compared to the average citizen’s earnings, prompting discussions around the broader implications of the CEO pay gap. As these leaders earn magnitudes greater than even the average full-time Australian, it underscores a critical point: economic disparity exacerbates societal divides. Addressing wage inequality requires not just policy changes but a shift in public perception regarding what constitutes appropriate compensation for different roles, particularly in leadership.
The Gender Pay Gap and Economic Disparity
The gender pay gap represents a significant dimension of wage inequality that continues to plague Australian society. Despite advancements toward equality, women still earn considerably less than their male counterparts, contributing to the broader pattern of economic disparity. Studies show that even as women make strides in the workplace, achieving better representation in various sectors, the pay differential remains stubbornly high. With a forecasted two-decade timeline until equal pay is reached, this persistent gap highlights the systemic barriers that continue to disadvantage women, particularly in leadership roles.
Moreover, the situation is complicated by other layers of inequality, such as unpaid work and caregiving responsibilities that disproportionately fall on women. These economic barriers hinder women’s professional growth and ultimately affect their financial security once they reach retirement age. Elevating the conversation about the gender pay gap is imperative for fostering social justice and economic equity. Addressing these issues can propel Australia toward a more inclusive future where every individual, regardless of gender, can thrive financially.
Impacts of Wage Inequality on Social Justice
Wage inequality in Australia not only highlights economic injustice but also reflects the broader implications for social coherence. The disparity between high earners and lower-income earners creates fissures in society, undermining social stability and cohesion. As those with the least earn insufficient incomes to effectively cover essential living costs, the impact is seen in increased poverty and social unrest. This reality starkly contrasts with the widespread belief that hard work and dedication alone suffice to guarantee a comfortable living, emphasizing the need for a renewed commitment to social justice as a foundational pillar of Australian society.
Moreover, tackling wage inequality aligns with efforts toward social justice and equity. It calls for comprehensive policies that not only increase base wages and build a fair minimum wage structure but also provide educational and career development opportunities for all Australians. By addressing the root causes of inequality, the nation can begin to rectify the imbalances that lead to disenfranchisement and social division, striving toward a society where everyone has the opportunity to succeed.
Exploring Economic Disparity Through Education
Economic disparity frequently intertwines with educational access and achievement in Australia. The Global Social Progress Index highlights that despite the nation’s wealth, access to quality education is unevenly distributed, further entrenching inequality. Individuals from lower socio-economic backgrounds often face barriers to educational opportunities, stifling upward mobility and perpetuating cycles of disadvantage. Recognizing the critical role education plays in mitigating income inequality is essential for creating a fairer society.
To bridge the gap in educational attainment, Australia must invest in targeted support programs, scholarship opportunities, and resources for disadvantaged communities. By ensuring that all children, regardless of their socio-economic status, have access to high-quality education, there is a greater chance of leveling the playing field. Breaking the cycle of economic disparity through education not only benefits individuals but fosters societal growth, leading to a more equitable economy for future generations.
The Role of Policy in Addressing Wage Disparities
Effective policy intervention is critical for addressing wage disparity in Australia. Policymakers must develop comprehensive strategies aimed at creating a more equitable distribution of income across various sectors. This includes implementing living wage standards, enforcing regulations for fair pay practices, and promoting workplace diversity. By reforming economic policies and prioritizing equitable practices, the government can begin to mitigate income inequality and its negative effects on society.
Additionally, it requires ongoing dialogue among stakeholders, including businesses, labor unions, and the community, to foster a culture of fairness and accountability. Policies should not only focus on improving compensation for the lowest earners but also ensure that the growth of top executive salaries does not overshadow the need for equitable pay across the workforce. Through unified efforts and committed policy reforms, Australia can pave the way towards a more inclusive economy that values every worker equally.
First Nations Australians and Wage Inequality
Wage inequality impacts various demographics in unique ways, particularly First Nations Australians, who face systemic barriers that exacerbate these disparities. Historical injustices and ongoing discrimination contribute to significant economic disadvantages, leading to disproportionate levels of unemployment and poverty within these communities. The intersection of cultural identity and economic opportunity presents unique challenges in addressing wage inequality, calling for targeted initiatives that respect and empower First Nations voices in discussions surrounding economic reforms.
To create sustainable changes that uplift First Nations Australians, community-led approaches must be prioritized. This involves investing in educational programs, job training, and support systems designed to enhance economic participation. Not only is this equity essential for economic justice, but it promises broader societal improvements as well, fostering an inclusive environment where all Australians, irrespective of their background, can thrive together.
Elevating the Discourse on Income Inequality
The conversation around income inequality and wage disparities must evolve to encompass broader societal narratives and lived experiences. It is increasingly clear that income inequality is not just an economic issue but also a social one, impacting people’s perceptions of opportunity and their sense of belonging within society. As Australians engage with these issues, it becomes crucial to shift the narrative away from individual blame to collective responsibility for enacting change.
Raising awareness through community engagement and education can empower citizens to advocate for more equitable policies. By fostering discussions around the experiences of those facing economic hardship or discrimination, the community can work together to devise solutions that promote fairness. Engaging diverse voices in these conversations not only highlights the multifaceted nature of income inequality but also inspires collective action towards achieving a just society.
The Future of Wage Equality in Australia
The path towards wage equality in Australia will require sustained effort, commitment, and innovative solutions. As more Australians recognize the severe implications of wage inequality, there is hope for a future where economic justice prevails. This includes potential shifts in public policy, workplace norms, and societal expectations regarding compensation and equity. Continued advocacy is crucial for ensuring that wage disparity remains a priority on the national agenda.
Moreover, harnessing technology and data-driven insights will help inform equitable practices and policies. By leveraging these resources, Australia can strive to build a future economy that values fairness, fosters opportunity, and reduces economic disparity at every level. With clear intentions and collaborative efforts, countries can move toward not just addressing wage inequality, but actively working toward a holistic vision of social justice in the economic landscape.
Advocating for Change: The Role of Citizens in Reducing Inequality
Citizens play a vital role in addressing wage inequality through collective action and advocacy. Grassroots movements have historically been at the forefront of calls for economic justice, highlighting issues that must be confronted to drive systemic change. As awareness of income inequality grows, the need for community engagement and activism is more critical than ever. By standing in solidarity with those affected by wage disparities, individuals can amplify their voices and influence policy decisions that promote a more equitable society.
Furthermore, citizen engagement is essential for fostering a culture of accountability and transparency in workplaces and at governmental levels. Advocacy initiatives focused on economic justice can mobilize support from various sectors, thereby pushing for reforms that enhance labor rights and fair compensation. In this way, the push for wage equality can empower individuals and communities to actively participate in reshaping the economic landscape toward a more inclusive future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors contributing to wage inequality in Australia?
Wage inequality in Australia is primarily driven by several factors including the gender pay gap, economic disparity across different regions, and the significant differences in earnings between CEOs and average workers. The gender pay gap reflects the systemic barriers women face in the workforce, leading to lower pay compared to their male counterparts. Additionally, economic disparities are exacerbated by varying levels of access to quality education and employment opportunities, which further influence income inequality.
How does the gender pay gap impact wage inequality in Australia?
The gender pay gap plays a critical role in wage inequality in Australia, where women earn substantially less than men for similar roles. Despite progress, research shows that achieving equal pay may take nearly two decades. This gap not only affects immediate earnings but also contributes to lower superannuation balances for women, resulting in economic instability, especially in retirement. Addressing the gender pay gap is essential for reducing overall wage inequality in Australia.
What is the CEO pay gap and how does it relate to wage inequality in Australia?
The CEO pay gap refers to the disproportionate earnings of company executives compared to average workers. In Australia, CEOs earn around 103 times more than the average full-time salary, a stark contrast to the public’s perception. This significant differential not only highlights the extreme wage inequality in Australia but also raises questions about social justice and economic equity within the corporate landscape.
How does Australia rank internationally in terms of income inequality?
While Australia ranks impressively in the Global Social Progress Index, with a position of 12 out of 170 countries, the report sheds light on concerning levels of income inequality. Factors such as the CEO pay gap and the gender pay gap highlight the disparities faced by various demographics. As the wealth of the nation grows, the benefits are not shared equally, indicating that while our overall economy appears strong, significant work remains to address income inequality.
What measures can be taken to reduce wage inequality in Australia?
To reduce wage inequality in Australia, comprehensive policy changes are needed, including promoting equal pay for women, enhancing workplace flexibility, and increasing access to quality education and childcare. Implementing strategies that address economic disparities across regions and demographics, such as support for disadvantaged communities and marginalized groups, will be essential for fostering a more equitable economy.
How does wage inequality affect social justice in Australia?
Wage inequality directly impacts social justice in Australia by perpetuating economic disparities among different demographics, including gender, ethnicity, and socio-economic backgrounds. As wage gaps persist, disadvantaged groups face barriers to social mobility, leading to a cycle of poverty and limited opportunities. Addressing wage inequality is crucial for achieving greater social justice and ensuring that all Australians have access to the resources and opportunities necessary for a fulfilling life.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Wage Inequality Understanding | Australians underestimate the number of low earners and overestimate those in the top 30% of earners. |
| CEO Earnings Disparity | CEOs earn 103 times the average worker’s salary; public perception is 7.1 times. |
| Gender Inequality | Significant wage gap persists; equal pay not expected for almost 20 years. |
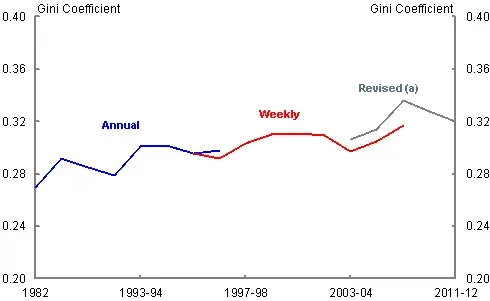
| Economic Inequality Trends | Economic inequality at its highest since 2001; richest incomes growing faster. |
| Impact on Specific Groups | Disadvantage affects First Nations, LGBTQI, disabled individuals, etc. |
| Social Indicators | Australia ranks poorly on diet, education access, and housing affordability despite high overall wealth. |
Summary
Wage inequality in Australia is a pressing issue that highlights the disparity in income distribution across various demographics. While Australia is often portrayed as a prosperous nation, the reality shows a significant gap between the high earners and the rest of the population. Increasing awareness and actionable measures are essential to bridge this divide and promote a more equitable society.