Whole-person health is at the forefront of a revolutionary initiative launched by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), aiming to reshape our understanding of overall well-being. This innovative approach transcends traditional biomedical research, emphasizing the importance of viewing individuals holistically, integrating multiple determinants of health. By leveraging the latest findings in integrated health research, the NIH is committed to developing a comprehensive model that emphasizes healthy physiological function across all body systems. Complementary health strategies, including lifestyle modifications such as nutrition and physical activity, will be instrumental in promoting enhanced health outcomes. This initiative signifies a pivotal shift towards a more interconnected perspective of health that has the potential to redefine patient care and research methodologies.
The NIH’s landmark project on whole-person health introduces an integrative strategy that prioritizes well-rounded wellness over isolated medical treatment. By exploring the connections between various physiological functions, this initiative seeks to create a comprehensive ‘health map’ that reflects the intricacies of human anatomy and its associated systems. In doing so, it aligns with emerging trends in health sciences that promote a multi-faceted approach to well-being, considering psychological, physical, and social factors in tandem. This holistic health framework not only enhances our understanding of individual health variations but also fosters a more proactive stance towards disease prevention and health optimization. As research deepens in areas like complementary health techniques and lifestyle interventions, the pursuit of a fully integrated health perspective promises to enhance quality of life for many.
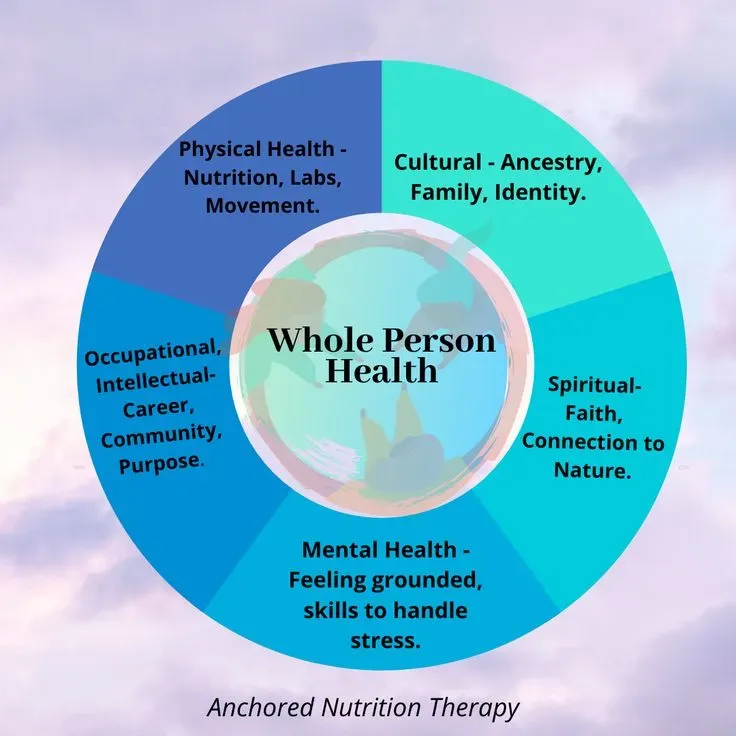
Understanding Whole-Person Health
Whole-person health encompasses more than just treating isolated symptoms or ailments; it represents a holistic consideration of an individual’s well-being. This approach integrates various dimensions of health—physical, mental, emotional, and social—recognizing that these factors are intertwined and essential for achieving optimal health outcomes. Emphasizing healthy physiological function, the whole-person model encourages people to engage in comprehensive lifestyle modifications, including balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and effective stress management techniques.
The NIH’s commitment to whole-person health aims to shift the paradigm of health research towards a system that considers the interconnectedness of bodily systems rather than focusing solely on specific organs or diseases. By integrating multiple health strategies, including those from complementary health modalities, researchers and healthcare providers can better understand how fostering healthy behaviors impacts overall health. This comprehensive view paves the way for innovative treatments that target health improvement from every angle.
The NIH Health Initiative: A Shift in Research Focus
The National Institutes of Health’s landmark initiative to promote whole-person health represents a paradigm shift in health research and understanding. Traditionally, biomedical research has zeroed in on specific diseases or organs, often neglecting the holistic nature of health itself. With the launch of this initiative, the NIH aims to consolidate a wide array of scientific knowledge into an integrated health research framework that acknowledges the dynamic interplay between various physiological and psychological factors contributing to health outcomes.
This five-year initiative will see the NIH weaving a network of interconnected data drawn from various factors such as clinical measures like blood pressure and glucose levels, combined with holistic health insights. By prioritizing a whole-person approach, the NIH endeavors to enhance not only scientific inquiry but also clinical application. This innovative framework will ultimately provide healthcare professionals with the tools needed to foster healthier populations through comprehensive research and implementation of effective health strategies.
The Importance of Healthy Physiological Function
Healthy physiological function is at the core of the NIH’s initiative to promote whole-person health. When physiological functions operate optimally—such as cardiovascular health, metabolic processes, and muscle strength—it supports not only physical health but also psychological and social well-being. Understanding how these functions interact is vital for developing comprehensive health interventions that transcend the limitations of traditional healthcare models.
Integrative health research within this initiative will focus on elucidating the relationships among various physiological markers and overall health. This scientific exploration aims to identify the underlying mechanisms that govern health outcomes, which can help pinpoint specific interventions needed to uplift individuals’ quality of life. As researchers develop a robust knowledge network grounded in healthy physiological function, they can tailor evidence-based strategies to maintain and improve health in diverse populations.
Complementary Health Strategies in a Whole-Person Framework
Complementary health strategies play a significant role in enhancing whole-person health, providing a range of options that can be integrated alongside conventional healthcare practices. These strategies, which may include therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, and nutritional counseling, align with the NIH’s whole-person approach by addressing not only physiological conditions but also emotional and mental health components. As part of this new initiative, the incorporation of complementary health practices is being encouraged to create individualized, multifaceted treatment plans.
The NIH’s commitment to exploring complementary health strategies aligns with their mission to support comprehensive health research. By investigating how these various modalities contribute to whole-person health, the NIH aims to provide healthcare practitioners with a toolkit of diverse approaches. This will enable them to better cater to patients’ unique health needs and preferences, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and a more rounded understanding of health management.
Building a Comprehensive Model of Whole-Person Health
The development of a comprehensive model of whole-person health is central to the NIH’s initiative, focusing on establishing a detailed map of how various body systems function together. This model will draw from advances in integrated health research, leveraging existing knowledge bases such as the NIH Human Reference Atlas and HuBMAP. By correlating clinical measures with physiological functionality, the NIH hopes to paint a more complete picture of how health operates on an individual level.
As researchers collaborate to enhance this model, they will explore the mechanisms that lead to health decline and the potential pathways for restoration. A well-structured health model will not only advance scientific knowledge but also serve as a practical framework for healthcare professionals. By understanding the interconnectedness of physiological functions, practitioners can better devise integrative treatments that promote sustainable health and wellness.
Innovations in Health Research and Data Integration
The NIH initiative aims to harness new technological advances for innovative health research. By utilizing cutting-edge data integration techniques, researchers can analyze large volumes of complex data relating to whole-person health. This will help them identify trends and insights that may have previously gone unnoticed within traditional research frameworks. Data integration is particularly pivotal as it allows for cohesive examination of health across multiple dimensions, crucial for understanding the complex realities of health and disease.
As researchers gather more scientific data at an unprecedented rate, the need for effective data integration becomes increasingly urgent. The initiative will push for collaborations across disciplines and utilize shared networks to ensure that new findings are synthesized effectively. Properly integrated data will pave the way for breakthroughs in understanding health dynamics, affording researchers the necessary insights to explore inquiries that encompass the full spectrum of whole-person health.
Understanding the Role of Stress Management in Health
Stress management is a crucial element of whole-person health, as chronic stress negatively impacts various physiological functions. The NIH’s initiative recognizes that emotional and psychological factors contribute significantly to overall health. Effective stress management strategies, including mindfulness practices, cognitive-behavioral techniques, and physical fitness, can dramatically enhance an individual’s capacity to maintain healthy physiological and mental states.
By emphasizing the importance of stress management within their research framework, the NIH aims to provide comprehensive resources and strategies for promoting resilience and well-being. Researchers will explore how integrating stress reduction practices within broader health interventions can lead to improvements in both mental and physical health, creating a holistic approach that recognizes the mind-body connection.
The Future of Whole-Person Health Research
The future of whole-person health research holds immense promise as the NIH continues to explore innovative ways to integrate knowledge from various health disciplines. This initiative reflects a growing recognition of the necessity for a comprehensive understanding of health that accounts for all factors influencing well-being. The application of a whole-person approach not only addresses existing health disparities but fosters a culture of proactive health optimization.
As the NIH advances into subsequent phases of its research initiative, the establishment of extensive collaborations and sharing of findings is anticipated. Researchers, practitioners, and policymakers will be encouraged to engage in dialogue that furthers understanding, ensuring the development of effective health policies and interventions. The future landscape of health research will likely transform, moving away from siloed studies and towards a more integrated, outcome-focused approach to health and wellness.
Empowering Individuals Through Informed Health Choices
Empowerment through informed health choices is a cornerstone of the NIH’s whole-person health initiative. By providing individuals with comprehensive information about how different aspects of health interconnect, people can make better choices about their lifestyle and wellness strategies. This shift towards self-advocacy helps individuals take charge of their health and encourages them to engage actively in preventive measures that support their overall well-being.
As part of this initiative, educational resources aimed at increasing public awareness around whole-person health will be crucial. By promoting access to knowledge regarding physiological health, complementary strategies, and effective stress management techniques, individuals from all backgrounds can enhance their understanding of health dynamics. This empowerment ultimately leads to improved health literacy and allows people to navigate their health journeys with greater confidence and efficacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is whole-person health according to the NIH health initiative?
Whole-person health, as defined by the NIH health initiative, emphasizes viewing individuals as complete systems rather than disconnected organs or systems. It encompasses various factors like mental, emotional, and physical health, integrating lifestyle interventions such as diet, exercise, and stress management to improve overall health outcomes.
How does the NIH’s integrated health research project aim to enhance whole-person health?
The NIH’s integrated health research project seeks to enhance whole-person health by creating a comprehensive knowledge network that connects physiological functions with clinical measures. This initiative will leverage existing scientific knowledge to build interactive models that account for the complexity of health, encouraging a holistic view of well-being.
What are some examples of complementary health strategies in the context of whole-person health?
Examples of complementary health strategies within the whole-person health framework include nutritional counseling, physical activity programs, mindfulness practices, and stress management techniques. These strategies support healthy physiological function by addressing both mental and physical health aspects, promoting overall wellness.
Why is research into healthy physiological function important for whole-person health?
Research into healthy physiological function is crucial for whole-person health because it helps identify the interconnectedness of various bodily systems. Understanding these connections enables researchers to develop effective interventions and treatments that consider the whole individual, leading to better health outcomes and disease prevention.
What role does the Whole Person Reference Physiome play in integrated health research?
The Whole Person Reference Physiome will serve as a foundational model in integrated health research, helping researchers visualize and comprehend how different physiological functions interact. It will facilitate the exploration of health decline factors and the mechanisms necessary for health restoration, thereby advancing knowledge in whole-person health.
How does the NIH initiative plan to collect and utilize human data for whole-person health research?
The NIH initiative plans to collect and utilize human data by correlating common clinical measures—such as blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and cholesterol—with major physiological functions. This data will enrich the existing knowledge framework, enabling the development of effective interventions that promote whole-person health.
What scientific inquiries does the NIH anticipate from their whole-person health initiative?
The NIH anticipates that their whole-person health initiative will lead to a variety of scientific inquiries regarding health dynamics, the interplay between different body systems, and innovative approaches to enhance overall well-being. This research will encourage a shift in focus from disease-centric studies to a more integrated understanding of health.
Where can I find more information about the NIH’s whole-person health research program?
You can find more information about the NIH’s whole-person health research program by visiting the NIH Research Portfolio Online Reporting Tools (RePORT) website at [this link](https://reporter.nih.gov/search/NHCW3mdunUCF3ULUAvilYQ/project-details/11224772#description), where you can explore project specifics and updates.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| NIH Landmark Project | The NIH has launched a new initiative focusing on whole-person health. |
| Whole-Person Health Concept | Addresses health beyond individual organs, taking a holistic view of the individual. |
| Research Focus | Improving understanding of healthy functioning across various body systems and their interactions. |
| Five-Year Initiative | Includes multiple phases and aims to create a comprehensive model of human physiology. |
| Data Integration | Links existing data with new findings to enhance understanding and research capabilities. |
| Whole Person Reference Physiome | Aims to create a detailed map that integrates the anatomy and function of the body. |
| NCCIH Role | Conducts research on complementary health approaches within the whole-person health framework. |
Summary
Whole-person health is a revolutionary approach that emphasizes the importance of viewing health in a holistic manner. The recent NIH initiative marks a significant advancement in this field by exploring not just the individual components of health, such as specific organs or diseases, but the intricate connections between various physiological systems. This initiative promises to enhance our understanding of health and disease while promoting integrative health practices that benefit individuals comprehensively. As research progresses, it will pave the way for a more complete model of health, fostering a deeper understanding of how lifestyle and environmental factors can influence overall wellness.