Canada Housing Crisis: Rethinking Wealth and Opportunity
The Canada housing crisis has reached critical levels, impacting first-time home buyers and young families across the nation. Rising property prices are exacerbating wealth inequality in Canada, leaving many feeling hopeless about their homeownership dreams. With soaring rents and stagnant wages, young Canadians are struggling to build generational wealth, often relying on financial support from their families to secure housing. Tax reforms in Canada are urgently needed to address these disparities, allowing aspiring homeowners to obtain affordable housing without incurring crippling debt. As the country grapples with this daunting crisis, innovative housing crisis solutions will be essential to pave the way for a future where hard work leads to prosperous living conditions for everyone.
The pressing issue of housing affordability in Canada has become a topic of increasing concern, especially for the younger population seeking to establish their roots. As urban centers see a rapid escalation in property values, many potential homeowners find themselves caught in a cycle of wealth disparity that makes owning a home seem nearly impossible. The need for comprehensive tax adjustments is evident as young workers face daunting obstacles to achieving stability through home ownership. By exploring alternatives for easing the burden on first-time home buyers, Canada could unlock pathways to economic empowerment and a brighter future. Addressing this housing dilemma not only requires policy changes but also a shift in how society perceives and manages wealth distribution.
Understanding Canada’s Housing Crisis
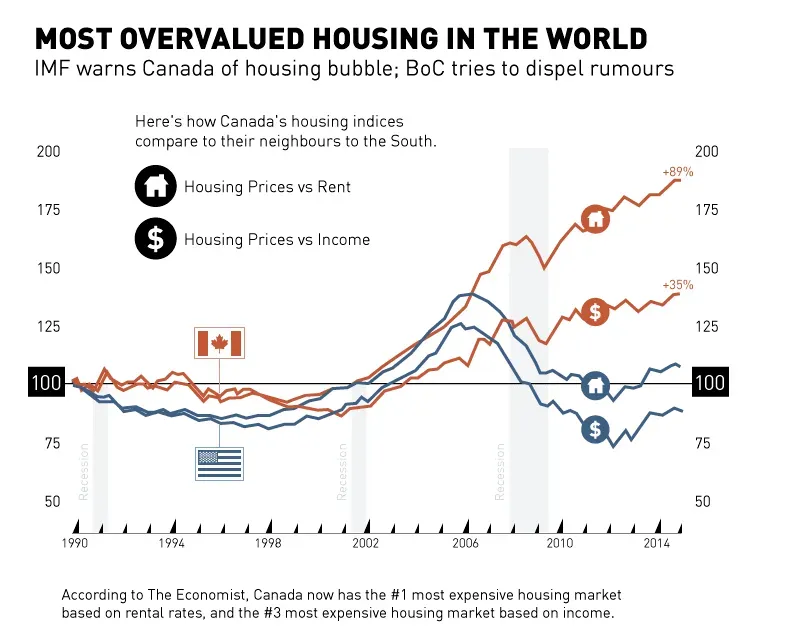
Canada’s housing crisis is a pressing issue affecting countless citizens, particularly younger generations struggling to achieve home ownership. As urban development continues to soar, the financial gap between wages and housing prices widens, creating a massive barrier for first-time home buyers. Many young Canadians find themselves trapped in a cycle of renting, unable to gather sufficient savings for a down payment due to exorbitant rent and living expenses. The current state of the housing market not only jeopardizes individual financial stability but also poses significant threats to economic growth and societal wellbeing.
Contributing to this housing crisis, wealth inequality in Canada exacerbates the challenges faced by prospective home buyers. Those born into affluent families have a significant advantage, benefiting from generations of wealth that allow them to purchase homes without the struggles that many young adults face today. The disparity in wealth ownership shifts the perception of success and opportunity, hindering the ability of younger, hardworking Canadians to attain a piece of the ‘Canadian dream.’ This ongoing crisis requires serious attention to develop policies that offer fair access to home ownership for all citizens.
Tax Reforms: A Pathway to Housing Affordability
Revising Canada’s tax system is critical in addressing housing affordability and ensuring that hard work is rewarded fairly. Currently, higher taxation rates disproportionately burden younger workers, who are often subjected to the same tax brackets as those earning significantly more. This unfair taxation structure prevents them from building the generational wealth necessary to buy homes and invest in their futures. Advocates for tax reforms suggest implementing changes that provide tax relief specifically aimed at younger Canadians and first-time home buyers, offering deductions or exemptions that would make home ownership more attainable.
In addition to reconsidering personal income tax rates, the introduction of tax incentives geared toward renters could provide immediate relief in the housing crisis. Allowing individuals to deduct rent from their taxable income, similar to mortgage interest deductions in other countries, could lessen the financial strain on those still renting. Such measures could foster a pathway toward home ownership by enabling renters to save efficiently while alleviating some of the burdens of living expenses, thereby contributing to a more balanced economic landscape.
Wealth Inequality and Its Impact on Home Ownership
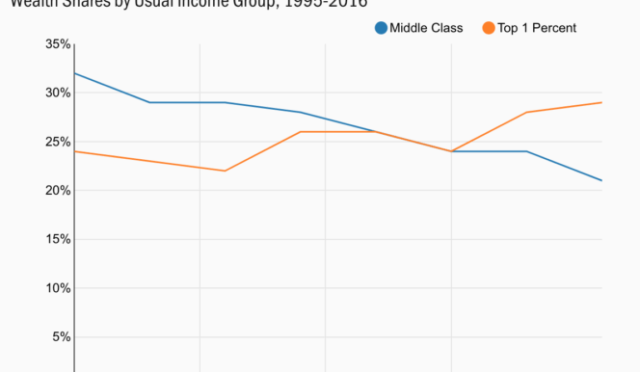
Wealth inequality in Canada plays a significant role in the housing crisis, creating disparities in the ability to purchase property among different demographics. Many young Canadians are unable to compete in a housing market dominated by well-off families and individuals who can leverage generational wealth. This lack of access to financial resources not only stymies home ownership aspirations but also diminishes the possibility of accumulating wealth for future generations. As a result, the gap between the wealthy and those striving for financial stability continues to widen, leading to profound social ramifications.
Efforts to tackle wealth inequality must focus on providing equitable opportunities for first-time home buyers. By promoting policies that empower young individuals through access to affordable housing and balanced employment opportunities, Canada can pave the way for a more inclusive society. Tax reforms that address these inequalities are crucial; they should not only alleviate the burdens facing younger generations but should also enhance overall economic health by fostering a generation capable of contributing actively to the housing market.
Empowering First-Time Home Buyers
First-time home buyers in Canada face overwhelming obstacles as they attempt to navigate an increasingly expensive market. With rising property values and challenging mortgage conditions, many aspiring homeowners find it nearly impossible to enter the market. Current policies often leave them at a disadvantage, especially when compared to buyers who benefit from family assistance or wealth accumulation. Addressing the unique challenges for first-time buyers can provide the necessary support for a generation eager to secure their future in the housing market.
One effective approach could involve implementing targeted incentives for first-time home buyers, such as tax credits or grants that can alleviate the initial costs associated with purchasing a home. These incentives could help reinvigorate a waning sense of hope among young Canadians and encourage them to invest in their futures. Encouraging local governments to create affordable housing initiatives specifically for first-time buyers is another potential solution to combat the existing barriers preventing youth from fulfilling their home ownership dreams.
A Fair Tax System for Generational Wealth
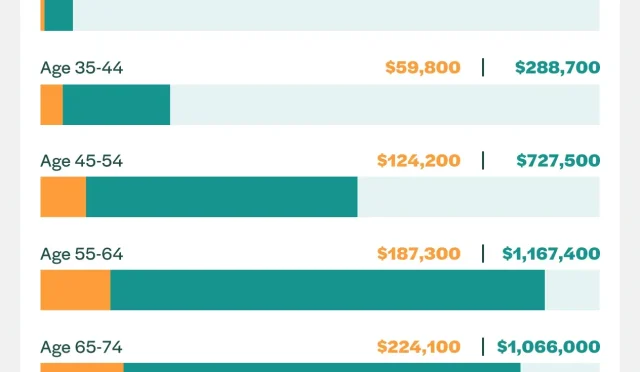
Reforming the tax system in Canada is essential for establishing a foundation that supports generational wealth growth across all demographics. As it stands, the tax structure often favors the wealthy, disproportionately impacting younger Canadians trying to establish their place in the housing market. High tax burdens on wages, coupled with the escalating cost of living, result in little opportunity for younger generations to build the wealth necessary for home ownership. To cultivate a more equitable system, rethinking the criteria defining wealth is critical.
An effective approach would be to create a tax system that acknowledges and supports the realities faced by younger earners, allowing them to invest in their future rather than being restrained by excessively high taxation. Policies that promote generational wealth, including tax breaks for long-term savings and investment, could provide the impetus needed for a new wave of economic participation. These reforms could help level the playing field, providing all Canadians with a fair chance to create wealth and secure stable housing.
Rethinking Solutions to Canada’s Housing Crisis
Proposing innovative solutions to Canada’s persistent housing crisis requires a comprehensive understanding of the root causes, including wealth disparity and complex taxation systems. Effective change hinges on a variety of factors, including more affordable housing options, adjustments in taxation policies, and support systems for younger generations. Engaging in community discussions and policy-making initiatives can foster the development of real solutions that not only consider the immediate needs of current home buyers but also address the sustainability of housing markets in the long term.
These discussions should not shy away from tackling challenging questions related to wealth redistribution and the redefinition of what constitutes wealth in Canada today. By prioritizing affordable housing solutions and equitable taxation measures, it’s possible to redirect resources to benefit those most affected by the ongoing housing crisis. In doing so, government and community leaders can work together to craft effective solutions that pave the way for a more inclusive future for all Canadians.
The Role of Government in Housing Affordability
Government intervention plays a critical role in addressing the housing crisis, particularly through the creation of policies that target economic support for vulnerable populations. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by younger Canadians and first-time home buyers, policymakers can craft strategies that create stability in the housing market. This includes exploring options like subsidized housing, investment in affordable housing development, and initiatives that improve accessibility to financial resources for new buyers.
Moreover, government accountability in ensuring fair taxation practices is essential to rebuilding the trust among younger Canadians. It is crucial for policymakers to remain attuned to the pressing needs of citizens, especially as it relates to housing affordability and wealth distribution. Establishing support systems that foster financial literacy and encourage responsible home buying can empower younger generations to become engaged participants in the economic landscape.
Addressing the Needs of Renters
In light of the housing crisis, it is vital to address the needs of renters who often face the brunt of economic pressures without the benefits of home ownership. High rental costs in cities across Canada have made it increasingly difficult for many young individuals to secure a decent living situation while saving for a future purchase. Expanding support mechanisms for renters, such as tax rebates or rent-to-own schemes, could be a practical avenue to bridge the gap between renting and owning.
Creating a supportive environment for renters is crucial for fostering a healthy housing market. This can include legislative measures that protect renters’ rights and encourage landlords to maintain reasonable rental practices. By providing structured support for a demographic that plays a vital role in the economy, Canada can address both current housing challenges and lay the foundation for future sustainable living.
Investing in Future Generations
Investing in future generations is a critical component of resolving Canada’s housing crisis. As the younger population faces mounting challenges in the real estate market, initiatives must focus on their empowerment through education and economic opportunity. Programs that enhance financial literacy and housing preparedness can equip young individuals with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of home ownership and wealth acquisition.
Furthermore, fostering partnerships between governmental agencies, educational institutions, and private sectors can create a robust support framework for young Canadians. These collaborations can focus on providing resources that facilitate success in achieving home ownership and encourage economic participation at earlier stages of life. By investing in youth initiatives, Canada can cultivate a new wave of responsible homeowners and economic contributors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors contributing to the Canada housing crisis?
The Canada housing crisis is primarily driven by wealth inequality, high taxation rates, and a lack of affordable housing options for first-time home buyers. Economic opportunities for young Canadians are diminishing, forcing many to live paycheck to paycheck due to soaring rent costs and high living expenses.
How does wealth inequality contribute to the housing crisis in Canada?
Wealth inequality in Canada intensifies the housing crisis as younger generations struggle to break into the property market. Many young Canadians face barriers to homeownership due to parents having acquired wealth and assets, leaving them at a disadvantage without financial support, thus delaying family formation and reducing the opportunity to build generational wealth.
What solutions are being proposed to address the Canada housing crisis?
Solutions to the Canada housing crisis include comprehensive tax reforms that benefit youngest Canadians, including tax incentives for first-time home buyers and renters. Proposals also suggest increasing tax exemption thresholds for lower-income earners, especially for young workers under 30, to help alleviate the financial strain associated with housing costs.
How can tax reforms impact first-time home buyers in Canada?
Tax reforms can significantly impact first-time home buyers in Canada by offering incentives such as tax deductions for rent or reducing taxes on income up to a certain threshold. These reforms would ease financial burdens and make homeownership more accessible, thereby contributing to a more favorable housing market for younger individuals.
What role does taxation play in the wealth inequality observed in Canada?
Taxation in Canada disproportionately affects younger workers and contributes to wealth inequality by imposing high rates on income that often reflects not just earnings but also assets. As younger generations face steeper taxes while trying to maintain a middle-class lifestyle, this creates a gap in wealth accumulation and limits their ability to purchase homes.
What are some practical solutions to support renters during the Canada housing crisis?
Practical solutions to support renters during the Canada housing crisis include allowing renters to deduct a portion of their rent on their taxes and extending renter-friendly alternatives to tax exemptions enjoyed by homeowners. These measures would alleviate financial pressure and promote a fairer taxation system for Canadians struggling with housing costs.
How can generational wealth be improved amidst the Canada housing crisis?
Improving generational wealth amidst the Canada housing crisis requires redefining wealth and implementing fair taxation methods. Focused efforts on creating affordable housing, supporting first-time home buyers with financial incentives, and ensuring equitable tax policies can help younger Canadians build wealth and secure homeownership.
What are the implications of the current tax system on young Canadians?
The current tax system in Canada disproportionately buries young Canadians under the weight of high taxation, limiting their financial freedom and ability to save for homeownership. This taxation model fails to reflect their actual earning capabilities and heights the challenges they face in achieving financial stability and wealth generation.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Rethinking Wealth | Canada’s housing crisis necessitates a new perspective on wealth that moves beyond income. |
| Tax Burden | Younger generations face high taxation rates that hinder their ability to achieve homeownership. |
| Income vs Cost of Living | Even families earning six-figure salaries struggle to afford basic necessities and housing. |
| Generational Equity | The current tax system disproportionately impacts younger Canadians trying to achieve the middle-class lifestyle. |
| CIBC Proposal | CIBC’s CEO suggests increasing tax exemption thresholds for younger workers to aid in savings. |
| Practical Solutions | Proposed tax incentives for renters and first-time home buyers could alleviate financial burden. |
Summary
The Canada housing crisis highlights the pressing need for a reassessment of how wealth is perceived and taxed across the nation. As high costs of living continue to outpace wages for many young Canadians, it becomes crucial to implement tax policies that do not penalize hard work but instead empower individuals to achieve homeownership and economic stability. Comprehensive reforms are needed to ensure that all Canadians can access the housing market without exorbitant financial strain.
#CanadaNews #HousingCrisis #WealthInequality #RealEstateCanada #EconomicOpportunity