Edge Computing: Revolutionizing Data Processing at the Source
Edge computing is transforming the way data is handled, processed, and delivered from millions of devices around the world. Unlike traditional cloud computing that relies heavily on centralized data centers, edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, improving response times and saving bandwidth. As industries increasingly demand real-time processing and ultra-low latency, edge computing has emerged as a game-changer in the tech landscape.
What is Edge Computing?
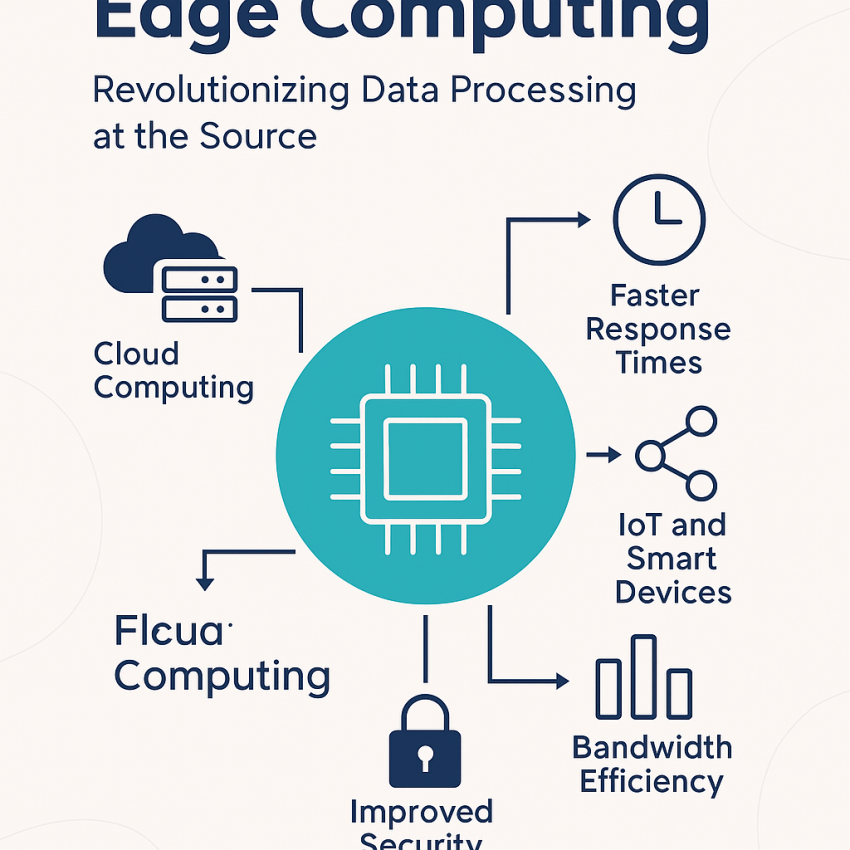
Edge computing refers to a distributed IT architecture where client data is processed at the edge of the network, as close to the originating source as possible. This setup contrasts sharply with centralized cloud systems, where data must travel long distances to be processed.
Key Features:
- Real-time data processing
- Reduced latency
- Improved bandwidth efficiency
- Enhanced data privacy and security
Why Edge Computing Matters
The demand for edge solutions is driven by:
- The explosion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- The need for instant processing in applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and remote healthcare
- Limitations of cloud computing in latency-sensitive use cases
Core Components of Edge Computing
1. Edge Devices
Includes sensors, smartphones, wearables, and IoT modules that collect and transmit data.
2. Edge Nodes/Gateways
Act as intermediaries, handling initial data processing and reducing load on cloud servers.
3. Edge Data Centers
Miniature data hubs placed closer to users, often regionally located for fast access.
4. Edge Analytics Software
Tools and platforms that analyze data locally and generate insights without sending everything to the cloud.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
- Smart Cities: Real-time traffic control, surveillance, and public safety systems
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring and diagnostics
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance, robotics, and automation
- Retail: Personalized customer experience and in-store analytics
- Autonomous Vehicles: Instant decision-making capabilities based on environmental inputs
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing | At or near data source | At centralized data centers |
| Latency | Low | Higher due to data transmission |
| Real-Time Analytics | Yes | Limited |
| Scalability | Moderate (regionalized) | High (centralized) |
| Data Privacy | Enhanced | May be at risk |
Benefits of Edge Computing
- Reduced bandwidth usage
- Real-time performance for critical applications
- Greater control over sensitive data
- Scalability for decentralized applications
- Cost savings by minimizing cloud dependency
Challenges and Considerations
- Managing distributed infrastructure
- Ensuring device compatibility and interoperability
- Security at multiple edge points
- Balancing cloud and edge workloads
The Future of Edge Computing
Edge computing is not a replacement for cloud computing—it’s a complementary technology. As 5G networks roll out and AI capabilities improve, the synergy between edge and cloud will define the next wave of digital transformation.
Conclusion: Bringing Intelligence to the Edge
Edge computing is revolutionizing how we think about data. By processing information closer to its source, it allows businesses and governments to act faster, smarter, and more securely. In a world that demands immediacy, edge computing is the cornerstone of modern, responsive tech infrastructure.
#EdgeComputing #SmartTechnology #IoTRevolution #RealTimeData #NextGenTech