Income Gap in Canada: Record High Disparity in 2025
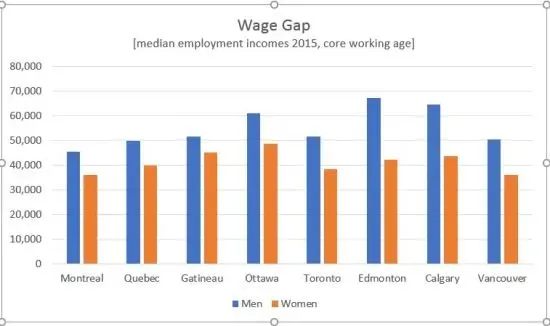
The income gap in Canada has reached alarming levels, highlighting a significant household income disparity that impacts millions across the nation. Recent reports from Statistics Canada reveal that the chasm between the wealthiest and the lowest income groups has widened to unprecedented proportions, reaching a staggering 49 percentage points as of early 2025. This worrying trend, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, demonstrates the growing income inequality in Canada, where top earners enjoy substantial gains from investments while lower-income households grapple with declining wages. In fact, the disposable income statistics indicate that those in the bottom 20 percent witnessed a minimal increase of just 3.2 percent year-over-year, contrasting sharply with the 7.7 percent growth experienced by the top 20 percent. As the nation continues to navigate the economic aftermath of the pandemic, understanding the nuances of income distribution becomes crucial in addressing these disparities and fostering a more equitable society.
Canada’s economic landscape is marked by an escalating income disparity, with recent data unveiling a stark contrast in earnings across different demographics. This gap highlights not only the struggles of households at the lower end of the income spectrum but also the disproportionate benefits enjoyed by wealthier Canadians, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Such income inequality underscores the pressing need for effective policy interventions aimed at improving income distribution. By examining household earnings and the overall financial wellbeing of citizens, we can better understand the implications of economic shifts on disposable incomes and the growing financial divides within the population. As discussions on economic reforms and social equity gain momentum, it becomes essential to address the fundamental causes of this widening chasm.
Understanding the Income Gap in Canada
The income gap in Canada has shown a worrying trend in recent years, particularly reaching alarming levels in the first quarter of 2025. According to Statistics Canada, the disparity between households in the highest and lowest income brackets has widened, with those in the top 40 percent enjoying a remarkably larger slice of disposable income. The figure stands at an astounding 49 percentage points, signifying a profound separation that has grown since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. This increasing divide highlights the significant challenges faced by lower-income households in achieving financial stability.
In a country like Canada, where social equality is highly valued, such marked income disparities evoke concerns about fairness and equity. The broader implications of this income inequality suggest that long-term economic mobility may be adversely affected. The pandemic has evidently exacerbated existing issues around household income disparity, as higher-income earners leverage investments and savings to enhance their disposable income, while those at the bottom of the income distribution struggle just to maintain their livelihoods.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Income Inequality
The COVID-19 pandemic has acted as a catalyst for widening income inequality in Canada, shedding light on how economic shocks disproportionately affect different segments of the population. While some households in the upper echelons of the income distribution have enhanced their fortunes, many others have encountered financial hardships. Notably, individuals in the bottom 20 percent of income earners saw their average wage decrease by 0.7 percent, showcasing the immense strains exerted by economic downturns.
Moreover, the pandemic has disrupted traditional employment patterns, leading to job losses and reduced hours for many lower-income earners. Simultaneously, as wealthier households capitalized on investment opportunities, their disposable income surged, reflecting a stark contrast in financial recovery post-pandemic. This two-tier recovery has raised pressing questions about policy responses needed to bridge income gaps, ultimately striving for a more equitable distribution of financial resources across Canadian society.
Trends in Canadian Income Distribution and Household Disparities
Examining Canada’s income distribution reveals a concerning trend regarding household income disparity, especially among lower-income groups. Statistics Canada underscores a growing inequality reflected in the gradual increase of disposable income among high earners, which stands in stark contrast to stagnation and decline for households with less economic clout. The reported increase in the wealth of the top 20 percent, growing by a striking 7.7 percent, poses serious implications for social mobility and cohesion within Canadian society.
Such alarming statistics indicate the urgency for policymakers to address the root causes of this widening gap. The increasing household income disparity not only erodes the quality of life for lower earners but also risks social discontent. Reducing this inequality is crucial for creating a balanced economy where all Canadians have the opportunity to thrive, regardless of their beginnings.
Statistics on Disposable Income in Canada
Disposable income statistics paint a vivid picture of economic well-being across various demographics in Canada. With the recent data from the first quarter of 2025 indicating that the top 20 percent of earners experienced a substantial increase in their disposable income, the implications for broader economic inequality become clearer. Understanding how disposable income shifts can inform strategies aimed at addressing income disparities is essential for fostering economic fairness.
Moreover, examining disposable income across different income brackets sheds light on the financial pressures faced by lower-income households. While the wealthier segment continues to see disposable income growth, those earning the least have often found it increasingly difficult to make ends meet. As cost of living rises, continued scrutiny and analysis of these statistics are vital for implementing effective measures to rectify income disparities and promote financial equity.
Analyzing Income Inequality Trends in Canada
Income inequality in Canada has evolved significantly over the years, marked by the pronounced differences between rich and poor households. The current trend showcases a stark reality where those in the higher income brackets have managed to increase their share of disposable income, while the less fortunate continue to face financial difficulties. Such inequities have implications that extend beyond mere statistics, impacting overall societal health and cohesion.
As noted in government reports, recognizing the patterns of income inequality is crucial for developing programs that could effectively support those affected. The continuous growth of income disparity illustrates the importance of ongoing policy evolution and intervention, particularly as Canada navigates the challenges posed by economic fluctuations and global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Exploring Factors Behind Income Disparity in Canada
Various factors contribute to the growing income disparity in Canada, each intertwining to create an increasingly complex socio-economic landscape. Education, access to stable job markets, and entrepreneurial opportunities are pivotal in determining income potential. Unfortunately, these opportunities are not uniformly accessible, leading to a persistent cycle of poverty for certain demographic groups.
Moreover, changes brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic have only exacerbated existing inequalities, making it harder for those already in vulnerable positions to recover. As observed, while job losses affected low-income individuals gravely, those with higher incomes generally found ways to navigate economic challenges, highlighting the systemic biases present within the labor market.
The Influence of Global Economic Events on Income Distribution
Global economic events have a profound impact on income distribution within Canada, as external forces often trickle down to affect local economies. The COVID-19 pandemic serves as a prime example of how such events can amplify income inequality, with lower-income households bearing the brunt of financial instability. The speed at which the economic landscape can shift requires both individuals and policymakers to adapt swiftly in order to protect those most vulnerable to change.
Additionally, the interconnectedness of economies means that fluctuations in global markets can directly influence Canadian households. While affluent households may benefit from economic booms through investments, the lower-income brackets often suffer significant setbacks during downturns. Understanding this dynamic is crucial in creating responsive policies that aim to mitigate the adverse effects of global economic shifts on the most affected communities.
Strategies to Address Income Inequality in Canada
Addressing income inequality in Canada requires a multifaceted approach that includes education, employment policies, and enhanced social safety nets. Strategies might include initiatives aimed at improving access to educational opportunities for marginalized groups, thus empowering them to break free from the cycle of poverty. Furthermore, restructuring employment policies to ensure fair wages across income brackets can contribute significantly to balancing household income disparity.
In addition to these measures, strengthening social safety nets to provide better support for those experiencing financial hardship is crucial. This could mean reevaluating government assistance programs to ensure they adequately meet the current needs of citizens, especially in the wake of economic disturbances such as the COVID-19 pandemic. By implementing these strategies, Canada can move towards a fairer and more equitable economic future.
The Future of Income Distribution in Canada
Looking ahead, the future of income distribution in Canada hangs in the balance, contingent upon how effectively policymakers respond to current disparities. Sustained attention to the income gap, particularly in light of rising living costs and the ongoing repercussions of economic upheavals, will be vital for ensuring equitable growth. It will require commitment and innovative solutions to tackle embedded inequalities that have been magnified over time.
As Canadians navigate the post-pandemic reality, there is an opportunity to reevaluate and reshape the socio-economic landscape towards inclusivity. The journey toward alleviating income inequality and addressing the significant household income disparity can lead to stronger communities and a more resilient economy overall.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current status of the income gap in Canada as of 2025?
As of the first quarter of 2025, the income gap in Canada has reached a record high, with a significant disparity between the highest and lowest income households. Statistics Canada reported that the share of disposable income between the top 40 percent and the bottom 40 percent of income distribution increased to 49 percentage points.
How has COVID-19 affected income inequality in Canada?
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated income inequality in Canada, as higher income households have benefitted from investments, while lower income households experienced wage declines. The disparity in disposable income has shown a continuous rise since the pandemic began.
What do recent disposable income statistics reveal about the income distribution in Canada?
Recent disposable income statistics indicate that the average disposable income for the top 20 percent of earners grew by 7.7 percent year-over-year, while those in the bottom 20 percent only saw a marginal increase of 3.2 percent, highlighting the widening income gap in Canada.
What factors contribute to household income disparity in Canada today?
Factors contributing to household income disparity in Canada include differing wage growth rates across income classes, investment benefits received by higher income households, and stagnation or decline in wages for lower income households.
Why is understanding income inequality in Canada important?
Understanding income inequality in Canada is crucial as it impacts social mobility, economic stability, and overall quality of life for citizens. The increasing income gap can lead to social tensions and hinder economic growth by limiting the purchasing power of lower income groups.
What measures are being taken to address the income gap in Canada?
Measures to address income inequality in Canada include policy debates on taxation, social welfare programs, and initiatives aimed at increasing minimum wages and employment opportunities, particularly for those most affected by the COVID-19 crisis.
How are changes in household incomes affecting the overall economy in Canada?
Changes in household incomes, especially the growing income gap, can affect consumer spending, economic growth, and social stability in Canada. The disparities in disposable income can lead to reduced economic participation among lower income households.
What trends are emerging in income distribution patterns in Canada?
Emerging trends in Canada’s income distribution patterns include an increasing concentration of wealth among higher income households and stagnating wages for lower income earners, further entrenching the income gap and highlighting the need for targeted economic policies.
| Income Group | Average Disposable Income Growth (%) | Average Wage Change (%) | Income Gap (Percentage Points) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottom 20% | 3.2 | -0.7 | 49 |
| Top 20% | 7.7 | N/A | 49 |
Summary
The income gap in Canada has reached alarming heights as of the first quarter of 2025. According to Statistics Canada, the disparity between the highest and lowest income households has expanded significantly, highlighting a growing economic divide. Households in the top 40 percent have seen a stark increase in disposable income, while those at the bottom have suffered declines in wages, exacerbating the income inequality within the nation. This ongoing issue reflects the broader economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has disproportionately affected vulnerable populations. Addressing the income gap in Canada will be essential to fostering a more equitable society.
#CanadaIncomeGap #WealthInequality #EconomicDisparity #IncomeInequality2025 #SocialJusticeCanada