Silicon Valley Economic Inequality: A Growing Crisis
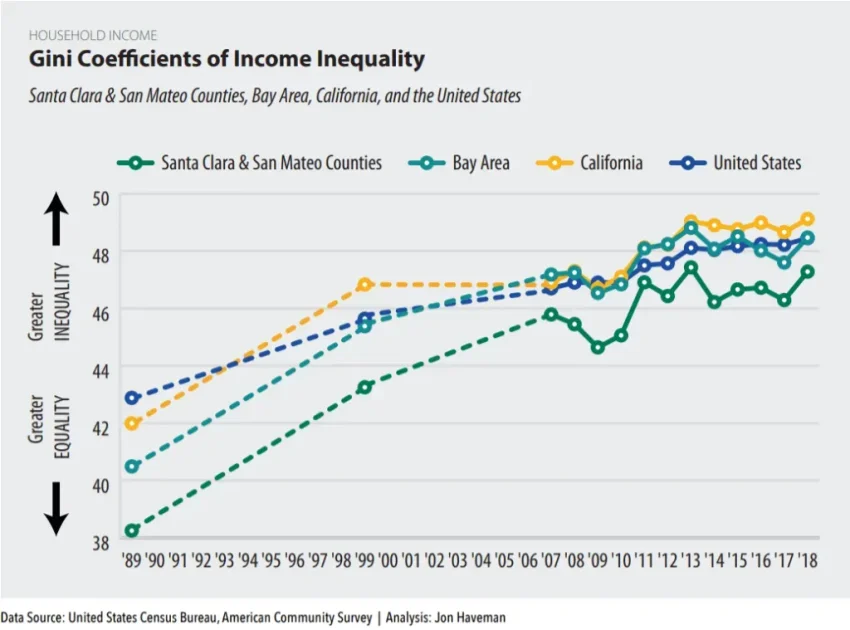
Silicon Valley economic inequality has reached alarming proportions, with a mere nine households amassing 15% of the region’s total wealth. This stark imbalance is highlighted in the recent “Silicon Valley Pain Index” report, which reveals that a shocking 0.1% of residents possess a staggering 71% of the region’s wealth, underscoring the critical wealth distribution in Silicon Valley. As the cost of living escalates, particularly in cities like San Jose where renters must earn over $136,000 just to afford an apartment, the struggle for affordable housing becomes increasingly desperate. The report shines a light on the unsettling rise of homelessness, with 54,582 low-income households trapped in a cycle of financial turmoil and escalating housing costs. Furthermore, racial inequalities in Silicon Valley persist, illuminating the urgent need to address systemic disparities in wealth and opportunity within this affluent tech hub.
The economic divide in Silicon Valley has become a pressing issue, often discussed as a reflection of broader societal disparities. This high-tech region, often viewed as a beacon of innovation and opportunity, paradoxically exhibits glaring gaps in wealth among its residents. Analyses, such as the Silicon Valley Pain Index, expose not only the wealth concentration among the elite but also the challenges faced by low-income families and marginalized communities, particularly regarding affordable housing in San Jose. As the cost of living continues to soar, it is critical to examine how these disparities affect various demographics, revealing significant racial inequalities in the labor market and beyond. Understanding the multifaceted nature of economic disparity in Silicon Valley is essential to fostering equitable solutions for those caught in a cycle of poverty and displacement.
Understanding Silicon Valley Economic Inequality
Economic inequality has reached alarming levels in Silicon Valley, where the stark divide is exemplified by the concentration of wealth among a select few households. Research from San Jose State University’s recent report reveals that just nine households command a staggering 15% of the region’s wealth, illustrating a level of wealth distribution that starkly contrasts with the economic struggles faced by many residents. Despite being a global tech hub, Silicon Valley is grappling with severe imbalances, where a mere 0.1% of the population is reported to hold 71% of the total wealth, raising questions about the sustainability and fairness of such a system.
This concentration of wealth in Silicon Valley not only represents economic disparity but also reflects systemic issues that have remained unaddressed over the years. As the 2025 ‘Silicon Valley Pain Index’ indicates, the inequality in wealth has widened at nearly double the rate of the national average over the past decade, marking a troubling trend for the region. Such statistics highlight a critical need for a thorough examination of the factors contributing to this economic divide, emphasizing the role of corporate practices, housing policies, and the overall cost of living in shaping the socioeconomic landscape.
The Silicon Valley Pain Index: A Measure of Inequality
The Silicon Valley Pain Index serves as a vital tool for understanding the lived experiences of those affected by economic inequality in the region. Released annually since 2020, the index aims to quantify both personal and community distress, providing a lens through which the systemic inequalities can be examined. This year’s report reveals a chilling statistic: the wealthiest households saw a $136 billion increase in their wealth, whereas 110,000 households reported near-zero assets, underscoring the chasm between the affluent and the struggling.
Moreover, the Pain Index not only tracks wealth distribution but also highlights the associated suffering experienced by those left behind in Silicon Valley’s economic boom. The report’s findings indicate that homelessness has surged by 8.2% since 2023, a troubling trend signaling the urgent need for effective policies aimed at addressing affordable housing in San Jose. As the cost of living continues to escalate, the index illustrates the critical influence of economic inequality on the quality of life for many residents in Silicon Valley.
Addressing the various layers of inequality reflected in the Silicon Valley Pain Index is pivotal for fostering a more equitable society. Through public awareness and policy intervention, it is crucial to confront the structural issues that perpetuate these disparities. Initiatives focusing on improving access to education, job opportunities, and equitable housing must be prioritized to ensure that all residents have a fair chance at success in this economically vibrant but often exclusionary region.
The Rising Cost of Living in Silicon Valley
The exorbitant cost of living in Silicon Valley has become a significant barrier for many residents, exacerbating existing economic inequalities. According to recent data, the average rent for an apartment in the region demands an astonishing annual salary of $136,532, positioning Silicon Valley as one of the most unaffordable places to live in the country. This situation has resulted in a growing number of families being pushed out of their homes, as they struggle to meet the demands of their financial obligations amidst soaring housing prices.
In addition to housing, essential living expenses continue to rise, further straining the finances of low-income families. With factors such as transportation, childcare, and healthcare costs also contributing to the high cost of living, many residents find themselves trapped in a cycle of financial instability. The disparity between incomes and living expenses in the area illustrates a dire need for comprehensive housing reforms and wage increases to alleviate the burdens faced by those on the lower end of the economic spectrum.
Affordable Housing Crisis in San Jose
The affordable housing crisis in San Jose reflects the broader challenges of inequality in Silicon Valley, highlighting how economic disparities manifest in access to basic needs. The recent report indicates that over 54,582 low-income households are struggling to find affordable housing within the city, exacerbating issues of homelessness and instability. The lack of accessible housing options is a pressing concern for families who are priced out of the market, forcing them to either stretch their budgets dangerously thin or face eviction.
Addressing the affordability of housing requires comprehensive strategies that focus on increasing the availability of low-income housing, implementing rent control, and supporting financially vulnerable families. Without actionable solutions, the ongoing housing crisis is likely to deepen, further entrenching social and economic inequalities in the region. A collaborative approach involving local governments, community organizations, and private sectors is vital to pave the way for long-term changes that prioritize equitable housing access.
Racial Inequalities in Silicon Valley
Racial inequalities remain a significant aspect of the socio-economic landscape of Silicon Valley, as highlighted by the disparities in income distribution among various racial groups. The Silicon Valley Pain Index has revealed staggering differences in earning potential, where Hispanic workers earn just 33 cents for every dollar that their white counterparts make. Such statistics illuminate the critical need for corporations and policymakers to address these inequities in the workforce, creating an environment that fosters inclusivity and equal opportunity for all.
Despite commitments from major tech companies to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion, the lack of representation in critical roles remains a sobering reality. For instance, only 3% of employees in research and development at Apple are Black, a clear indication of the barriers faced by minority groups in accessing high-paying positions in the tech industry. Addressing these racial disparities requires a concerted effort to implement recruitment strategies that focus on underrepresented communities, as well as advocating for equal pay and career advancement opportunities.
The Role of Local Government in Tackling Inequality
Local government plays a crucial role in addressing the systemic inequalities that characterize Silicon Valley’s economic landscape. Given the alarming findings of the Silicon Valley Pain Index, there is a pressing need for proactive measures to promote economic equity. Policymakers must prioritize affordable housing initiatives and wage reforms to help mitigate the financial burdens faced by residents. Additionally, local leaders should engage with community organizations to develop targeted programs that support low-income families, the homeless, and those who experience racial inequities.
Moreover, the government should investigate policies that have allowed wealth concentration to proliferate in the region. By promoting transparency and accountability among large corporations, local officials can advocate for fair labor practices, living wages, and sustainable economic development that uplifts the entire community rather than a select few. Only through collaborative efforts can Silicon Valley hope to create a more just and equitable society for all its residents.
Corporate Responsibility and Economic Equity
As the epicenter of the tech industry, Silicon Valley’s corporations bear a significant responsibility in contributing to economic equity and addressing the stark inequalities highlighted in the Silicon Valley Pain Index. Initiatives focused on corporate social responsibility (CSR) can play a vital role in reshaping the landscape and fostering a more equitable workforce. Companies must consider directing their resources toward community development projects, affordable housing efforts, and educational programs for disadvantaged youth to create a more inclusive environment.
Furthermore, corporations should reevaluate their hiring and wage practices to promote diversity and fair pay within their organizations. By taking a proactive stance in addressing racial and economic disparities in the workplace, tech giants can not only enhance their reputations but also contribute to a more balanced economy in Silicon Valley. Accountability and a commitment to fostering equitable growth are paramount in bridging the divide that currently exists within the region.
Social Initiatives for Reducing Disparities
Several social initiatives have emerged in Silicon Valley aimed at reducing economic disparities and promoting equity among residents. Nonprofit organizations and community groups have taken active steps to ensure that the voices of marginalized populations are heard and that their needs are addressed. Programs focused on workforce development, affordable housing advocacy, and financial education play a vital role in empowering individuals to improve their socio-economic circumstances.
Moreover, collaborations between local governments and community organizations focused on social justice are crucial in advocating for policies that protect low-income families and address the housing crisis. By promoting awareness and fostering partnerships, these initiatives aim to create systemic changes that uplift disadvantaged communities, while also emphasizing the importance of equitable wealth distribution in Silicon Valley.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Equity in Silicon Valley
Ultimately, the findings of the Silicon Valley Pain Index serve as a stark reminder of the urgent need for action to address economic inequality and ensure a fairer distribution of resources. The concentration of wealth among a few households amidst the struggles of countless others presents a moral imperative that cannot be ignored. As the region continues to grapple with rising living costs and deepening disparities, it is critical for stakeholders at all levels to unite in a collective effort for change.
This call to action necessitates comprehensive strategies that address affordable housing, racial inequalities, and the consequences of corporate practices that perpetuate wealth disparity. It is only through concerted efforts by local governments, businesses, and community organizations that Silicon Valley can begin to pave the way towards a more equitable and just future for all its residents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main findings of the 2025 Silicon Valley Pain Index regarding economic inequality?
The 2025 Silicon Valley Pain Index reveals alarming economic inequality trends, showing that just nine households control 15% of the region’s wealth, amounting to $683.2 billion. It also highlights that 0.1% of residents possess 71% of Silicon Valley’s wealth, indicating a widening wealth divide significantly outpacing national trends.
How does the cost of living in Silicon Valley impact affordable housing in San Jose?
The cost of living in Silicon Valley is extraordinarily high, with renters needing to earn $136,532 annually to afford typical apartments. This has exacerbated affordable housing issues in San Jose, where over 54,582 low-income households lack access to affordable homes.
What role do racial inequalities play in Silicon Valley’s economic disparity?
Racial inequalities significantly contribute to economic disparity in Silicon Valley, as evidenced by the fact that Hispanic workers earn only 33 cents for every dollar earned by their white counterparts. This stark wage gap reflects deeper systemic issues within the labor market and corporate structures.
What statistics illustrate wealth distribution in Silicon Valley?
Wealth distribution in Silicon Valley is starkly uneven, with just nine households holding 15% of the area’s total wealth. The 2025 Silicon Valley Pain Index indicates that 71% of regional wealth is concentrated in 0.1% of the population, highlighting extreme economic inequality.
How has the Silicon Valley Pain Index evolved over time in measuring economic inequality?
Since its inception in 2020, the Silicon Valley Pain Index has consistently quantified structured inequalities, reporting that economic divides have widened at double the national rate over the last decade. Its annual findings illustrate the ongoing challenges faced by marginalized communities.
What impact does the high cost of living in Silicon Valley have on homelessness?
The rising cost of living in Silicon Valley directly contributes to homelessness, which increased by 8.2% in 2024. With a significant portion of the population unable to afford housing, many residents face the risk of losing their homes.
Why is the rising cost of living in Silicon Valley notable compared to other global cities?
Silicon Valley’s cost of living is marked as one of the most unaffordable in the world, with San Jose ranking No. 4 globally for high living expenses, trailing only cities like Hong Kong, Sydney, and Vancouver. This has critical implications for housing accessibility and overall quality of life.
What efforts have been made to address the inequalities identified in the Silicon Valley Pain Index?
Though significant progress has been noted in some areas, such as decreased police use of force incidents and improved homelessness prevention services, systemic issues like wealth concentration and inadequate affordable housing persist and require ongoing efforts for meaningful change.
How do local policies in Silicon Valley affect economic inequality?
Local policies in Silicon Valley have failed to address economic inequality effectively, as no cities have increased minimum wage rates in the past three years, further exacerbating challenges faced by low-income families amidst rising living costs.
What are some signs of hope noted in the 2025 Silicon Valley Pain Index?
Despite the prevalent economic inequality, the 2025 Silicon Valley Pain Index reported some positive developments, including a reduction in police force incidents and increased initiatives aimed at enhancing environmental sustainability and prevention of homelessness.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Extreme Wealth Concentration | Nine households hold 15% of Silicon Valley’s wealth, with the richest controlling $683.2 billion. |
| Income Disparity | 0.1% of residents hold 71% of wealth; Hispanic workers earn 33 cents to every dollar earned by white workers. |
| Cost of Living | To afford rent in Silicon Valley, an income of $136,532 is required, making the region the most expensive in the U.S. |
| Homelessness Issues | Over 54,000 low-income households lack affordable housing, with reported homelessness increasing by 8.2%. |
| Police Violence | In 2024, Santa Clara County saw the highest number of deaths in police custody in two decades. |
| Improvements Noted | Some positive changes include reduced police use of force incidents and expanded homelessness prevention services. |
Summary
Silicon Valley economic inequality has reached unprecedented levels, highlighting a troubling divide in wealth and access to resources. This stark contrast between the affluent and the low-income communities signals a systemic problem that requires urgent attention. The findings from the 2025 “Silicon Valley Pain Index” expose the harsh reality faced by many residents, particularly regarding housing affordability and racial disparities in income. Although there have been some improvements noted, the persistence of homelessness and police violence underscores the ongoing struggles of those at the lower end of the economic spectrum. Addressing these inequalities is essential for fostering a more equitable and sustainable future for all residents.
#SiliconValleyInequality #EconomicDisparity #TechWealthGap #IncomeInequality #SocialJustice