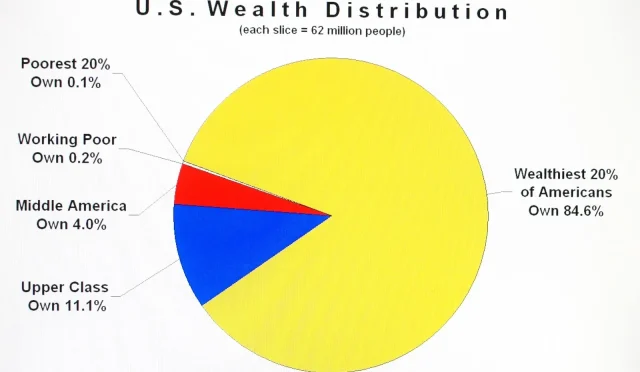
In light of the rising UK wealth inequality, the discussion around implementing a wealth tax on property has gained significant traction. This type of taxation can potentially serve as a crucial countermeasure to the escalating housing prices in the UK, addressing the financial imbalances that plague many citizens. By taxing wealth concentrated in property ownership, the government could leverage substantial resources to fund essential public services like healthcare and education, thus promoting social equity. Furthermore, property tax benefits could be designed to support low-income households, ensuring that the wealthy contribute their fair share towards community welfare. As the nation grapples with economic reforms, a wealth tax on property emerges not just as a fiscal necessity but as a pragmatic approach to redistributing resources for a more equitable society.
As the UK confronts challenges associated with wealth disparity, advocating for a property ownership tax appears increasingly relevant. This taxation strategy could play a pivotal role in addressing financial inequalities while providing necessary funds for vital services. By targeting the wealth accumulated through property, such a tax could facilitate improvements in community infrastructure and access to education. Furthermore, with soaring housing prices impacting affordability, this approach to wealth taxation could ease the burden on lower-income earners. In the broader context of economic reforms in the UK, adopting a property tax could lead to a more balanced and inclusive economic landscape.
The Case for a Wealth Tax on Property
In the UK, the disparity in wealth distribution has reached alarming levels, prompting discussions on the necessity of a wealth tax on property. Traditionally, property ownership has generated considerable wealth for individuals, often leading to significant financial advantages over those unable to enter the property market. This imbalance contributes to worsening wealth inequality and challenges the social fabric of the nation. By instituting a wealth tax on property, the government could harness substantial funds for public welfare, community development, and essential services, thereby addressing the urgent socio-economic issues facing the populace.
Countries around the world, such as France and Switzerland, have successfully implemented property taxes to counter wealth disparity and promote social equality. These examples illustrate the viability of a wealth tax as a mechanism for funding public goods and services, such as education and healthcare. Furthermore, this tax stands to alleviate the burden on lower-income families while also ensuring those who have significantly benefitted from property ownership contribute their fair share to society. As housing prices in the UK continue to soar, the incorporation of a wealth tax could ensure broader financial responsibility and encourage a more balanced approach to wealth distribution.
Addressing UK Wealth Inequality with Property Tax Reforms
Wealth inequality in the UK has become increasingly pronounced, with studies showing a growing divide between property owners and renters. The current tax system fails to adequately address the benefits enjoyed by property owners, leaving many communities without essential resources. Property tax reforms, specifically a wealth tax on property, could bridge this gap by reallocating financial resources towards underfunded public sectors. This approach not only targets the wealth amassed through property ownership but also enhances public infrastructure, ensuring that all citizens benefit from their collective contributions.
Additionally, with escalating housing prices, the disparity in access to home ownership has widened substantially. For many families, the dream of owning a home has become increasingly unattainable, leading to a rise in rental poverty. By implementing wealth tax measures on property, the government can generate much-needed funds to support affordable housing initiatives and other community-centric programs. Such reforms would not only aid in combating wealth inequality but also ensure that essential services are accessible to all, fostering a more inclusive society.
Rethinking Property Ownership Taxation in the UK Economy
As the UK economy grapples with various challenges, rethinking property ownership taxation becomes essential. Currently, those who own property benefit from capital gains that far outstrip inflation, often devoid of significant tax obligations relative to their wealth. A wealth tax on property could remedy this by creating a fairer taxation landscape where wealth generation through property ownership contributes effectively to the economy. Additionally, this could lead to increased social mobility by providing funds for education and job training programs aimed at empowering lower-income households.
In a country where housing prices continue to climb, the burden on those outside the property market grows heavier. A reformative approach to property taxation could alleviate financial pressures faced by renters while bolstering public service funding. Implementing a wealth tax not only realizes greater fiscal equity but also aligns with broader economic reforms necessary to secure a sustainable future for the UK. The positive implications of such reforms could help reverse the trend of wealth concentration and foster a more robust, equitable economy.
The Benefits of Property Tax in the Context of Economic Reforms
Through the lens of ongoing economic reforms in the UK, a wealth tax on property can be seen as a transformative tool. This proposal aims to tackle pressing issues like wealth inequality and inflation, providing a pathway to more equitable growth. The consistent rise in property values disproportionately benefits wealthier individuals and families, creating an environment where financial resources are inequitably concentrated. By implementing a wealth tax, these assets can be tapped to fund essential services that directly benefit society, thereby promoting fairness and accessibility in public goods.
Property tax benefits are not limited to generating revenue; they also instigate improvements in community integrity and resilience. A wealth tax could incentivize property owners to invest in their localities, understanding that their contributions will enhance community infrastructure and social services. With strategic allocation of tax revenues, local governments can address critical issues, such as housing shortages and underfunding of public sectors. Ultimately, the adoption of a wealth tax on properties aligns economic reform efforts with social equity, establishing a fairer society where all individuals have the opportunity to thrive.
Combatting Rising Housing Prices in the UK
Rising housing prices in the UK have been a significant factor contributing to economic stress for many families. As market conditions continue to inflate real estate valuations, younger generations find themselves priced out of home ownership, leading to increased rental demand and costs. A wealth tax on property could be a pivotal measure to combat these rising prices by redistributing wealth and enabling greater investment in affordable housing projects. Government funding generated through property taxes can be directed toward constructing low-cost housing, providing relief to struggling families and creating a more stable housing market.
Moreover, addressing rising housing prices through a wealth tax addresses not only financial accessibility but also social stability. When more citizens are enabled to secure affordable housing, the associated social benefits—such as reduced stress, improved health outcomes, and stronger community ties—become evident. A wealth tax could thus play a critical role in the broader economic strategy to alleviate housing challenges while promoting fairness and accessibility across societal strata. In tackling these issues, the UK can aim for a more resilient economy that prioritizes the well-being of its citizens.
Ensuring Long-Term Economic Resilience through Tax Reforms
As the UK navigates economic challenges, implementing a wealth tax on property can serve as a vital strategy for ensuring long-term resilience. Economic shocks, such as those seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlight the vulnerabilities in the existing financial system, particularly concerning wealth concentration. A wealth tax on property represents a more sustainable fiscal policy approach, providing the government with a continuous revenue stream to invest in public welfare and economic reform initiatives. This can help mitigate the impacts of future economic instability, fostering a more adaptable and responsive economy.
Furthermore, by embracing a wealth tax focused on property ownership, the government can signal a commitment to addressing wealth inequality while investing in human capital. This approach not only enhances the effectiveness of fiscal policy but also aligns with broader societal goals. A resilient economy thrives on equality and accessibility, and implementing property tax reforms could catalyze opportunities for those currently excluded from wealth generation. Through strategic economic policies backed by tax reform, the UK can build a more secure and prosperous financial future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the proposed wealth tax on property in the UK?
The proposed wealth tax on property in the UK would involve levying a tax on the value of real estate owned by individuals and families. This initiative aims to address wealth inequality by redistributing funds to support essential public services and community infrastructure.
How could a wealth tax on property help reduce UK wealth inequality?
A wealth tax on property could significantly reduce UK wealth inequality by taxing the accumulated wealth in real estate, which is a major source of wealth for many individuals. The generated revenue could be allocated to public services such as education and healthcare, thereby promoting a more equitable distribution of resources.
What are the potential benefits of implementing property tax benefits alongside a wealth tax?
Implementing property tax benefits alongside a wealth tax could encourage property ownership while ensuring that wealthier individuals contribute fairly. Benefits could include exemptions for first-time buyers or low-income households, striking a balance between promoting homeownership and generating necessary tax revenues.
How does a wealth tax on property relate to rising housing prices in the UK?
As housing prices in the UK continue to rise, a wealth tax on property could serve as both a measure to address wealth inequality and a method to manage housing affordability. By taxing high-value properties, the government could use the funds to subsidize housing initiatives that benefit lower-income families.
What economic reforms are needed to implement a wealth tax on property in the UK?
To implement a wealth tax on property effectively, economic reforms in the UK may include establishing clear valuation methods for properties, ensuring fair tax rates, and creating robust administrative frameworks to collect and manage the tax revenue. These reforms would help ensure that the tax system is equitable and efficient.
Can a wealth tax on property provide a sustainable revenue stream for the UK government?
Yes, a wealth tax on property can provide a sustainable revenue stream for the UK government, especially as property values appreciate over time. This tax can be adjusted annually based on real estate market trends, offering a reliable source of funding for essential services without overly burdening lower-income residents.
What are the challenges of introducing a wealth tax on property in the UK?
The challenges of introducing a wealth tax on property in the UK include potential pushback from property owners, concerns about valuation discrepancies, and the administrative burden of assessing and collecting the tax. Additionally, fear of discouraging property investment may also arise.
How does the concept of a wealth tax on property compare to other taxes in the UK?
A wealth tax on property differs from other taxes in the UK, such as income or capital gains taxes, by specifically targeting accumulated wealth in real estate. While income taxes focus on earnings, a wealth tax seeks to redistribute existing wealth, promoting social equity in the face of rising property ownership wealth.
What impact could a wealth tax on property have on community welfare in the UK?
A wealth tax on property could significantly enhance community welfare in the UK by generating funds for public services, infrastructure projects, and social programs. This investment could improve education, healthcare, and public amenities, ultimately benefiting society as a whole and reducing poverty levels.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Wealth Inequality Crisis | The UK is experiencing growing wealth inequality, necessitating new solutions. |
| Wealth Tax on Property | Implementing a wealth tax on property could generate financial resources for public needs. |
| Global Examples | Many countries have successfully implemented wealth taxes to promote fairness. |
| Impact on Community | Taxes on property can help redistribute wealth, fund education, healthcare, and infrastructure. |
| Economic Resilience | A wealth tax can align fiscal policy with social responsibility and aid in economic stability. |
| Sustainable Revenue Stream | Such taxes might provide a reliable revenue source amidst economic challenges. |
Summary
Wealth tax on property is a critical consideration in addressing the growing issue of wealth inequality in the UK. As traditional measures fall short, implementing this tax could ensure fair redistribution of resources while funding essential services like education and healthcare. In an era of soaring property values and rental distress, a wealth tax presents a viable solution that promotes community investment and fosters a more equitable economy. Furthermore, it aligns well with the government’s objectives to enhance economic resilience, ultimately leading to a fairer society.