Wealth transfer preparation is a crucial but often overlooked aspect of financial planning for families. As the Great Wealth Transfer unfolds, with an estimated $124 trillion set to be passed down from baby boomers to their heirs by 2048, the importance of inheritance planning becomes ever clearer. Many heirs may find themselves unprepared to manage their newfound wealth, highlighting the need for comprehensive family wealth management strategies. The process entails fostering financial literacy for heirs, guiding them through their beneficiary responsibilities, and encouraging open discussions about wealth and legacy. Without proactive measures, families risk facing conflict, mismanagement, or even squandering these substantial assets.
The process of preparing for the transfer of wealth encompasses various strategies aimed at ensuring a smooth transition of financial assets. This critical topic is often framed within the context of fiscal stewardship and estate preparation, where families engage in thorough discussions about asset distribution and inheritance frameworks. By emphasizing financial education and the responsibilities that accompany wealth, family members can forge a legacy that endures beyond their lifetime. It’s essential for both current asset holders and their heirs to communicate effectively about family finances, fostering a culture of understanding that respects both the legacy and the future. Addressing these issues before the transfer takes place can significantly reduce the likelihood of wealth loss across generations.
Understanding the Great Wealth Transfer
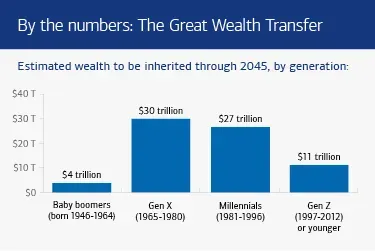
The Great Wealth Transfer refers to the unprecedented shift of wealth from older generations to their heirs, primarily driven by the financial assets accumulated by the baby boomers. With estimates suggesting that around $124 trillion will be passed down to heirs by 2048, the imperative question arises: are these future beneficiaries adequately prepared to inherit such substantial wealth? As an increasing number of individuals accumulate wealth, it’s essential to recognize the responsibilities that accompany these assets. Financial literacy and education are critical in this equation, ensuring that inheritors not only understand how to manage their newfound wealth but also respect and honor their family’s legacy.
One significant aspect of the Great Wealth Transfer is the potential for mismanagement and loss of wealth across generations. Studies, such as the one conducted by the Williams Group, indicate that nearly 70% of affluent families see a decline in their wealth by the second generation. This phenomenon highlights the importance of inheritance planning and proactive engagement among family members, addressing any underlying dynamics that may hinder open communication regarding wealth management. By facilitating discussions around financial stewardship, families can cultivate a culture of responsibility that empowers heirs, setting them up for long-term success.
Wealth Transfer Preparation: Key Steps to Take
The preparation for wealth transfer involves strategic planning that includes discussions about inheritance, estate management, and the various responsibilities that come with inheriting wealth. Families should prioritize transparent dialogues about their financial situation and long-term aspirations for their wealth. Implementing a structured plan that encompasses wills, trusts, and family meetings can significantly ease the transition for heirs, ensuring they are informed and ready to manage their inheritance effectively. Proactive measures taken by parents and grandparents can help cultivate a sense of financial responsibility among heirs, thereby promoting healthier relationships with wealth.
Additionally, it is crucial for families to recognize the role of financial advisors in this preparation. Engaging professional advisors can assist in mapping out complex family dynamics and addressing financial literacy for heirs. These professionals can provide tailored guidance about managing taxes, investments, and other financial obligations that heirs may face. Furthermore, involving a neutral party can mitigate potential tensions and foster open communication about wealth transfer, ultimately ensuring that the family legacy is passed down successfully.
The Importance of Financial Literacy for Heirs
Financial literacy is a vital component for beneficiaries, equipping them with the knowledge and skills necessary to manage and grow inherited wealth. Understanding concepts such as budgeting, investing, and tax implications can substantially impact how heirs utilize the wealth they receive and how they contribute to family wealth management. Families can help nurture this financial literacy by providing education and resources, including workshops, seminars, or one-on-one sessions with financial advisors to discuss inheritance planning. Emphasizing these resources early in the wealth transfer process can create a more financially competent generation.
Moreover, heirs should actively engage in their financial education, seeking out information and tools that can bolster their confidence in handling complex financial matters. By becoming savvy about different types of investment accounts, tax strategies, and even philanthropic opportunities, heirs not only prepare themselves to be responsible recipients but also play an integral role in preserving their family’s wealth across generations. This foundation can ultimately prevent the often-repeated cycle of wealth dilution that plagues many families.
Family Wealth Management: Building a Sustainable Legacy
Effective family wealth management is essential for ensuring that legacies are not only preserved but also grown over time. This requires a focused strategy that encompasses regular family meetings, clear communication regarding financial goals, and collaborative decision-making about investments and charitable contributions. By establishing a unified vision for managing family wealth, members can engage meaningfully with the assets and resources at their disposal, which solidifies their bonds and commitment to stewardship.
In addition, utilizing the expertise of family offices can provide tailored support for families navigating the complexities of wealth management. These entities often specialize in addressing various aspects of family finances—from tax planning to investment strategies—all while providing a platform for ongoing education and dialogue among family members. By fostering a proactive approach to family wealth management, heirs are better positioned to embrace their responsibilities and maintain a thriving financial legacy.
Beneficiary Responsibilities: A Guide to Ethical Stewardship
Becoming a beneficiary of a family’s wealth carries ethical responsibilities that extend beyond personal finance. Heirs must understand their duty to honor the intentions of their benefactors while making decisions that reflect integrity and an awareness of broader societal impacts. This includes careful consideration of how they allocate their inherited resources, from investments to charitable giving. Recognizing that their actions can influence the family legacy is crucial for responsible wealth stewardship.
Moreover, beneficiaries should aim to cultivate a mindset of gratitude and transparency in their financial dealings. Engaging in conversations about their intentions with family members can help to affirm shared values and create a collaborative approach to wealth management. Ultimately, by perceiving wealth as not merely a personal asset but a collective responsibility, beneficiaries can contribute positively to their family’s long-term vision and societal impact.
Navigating Family Dynamics During Wealth Transfer
Wealth transfer can sometimes bring underlying family dynamics to the forefront, leading to tensions or disputes over assets and responsibilities. To mitigate conflicts, establishing open lines of communication among family members is paramount. Discussions regarding wealth should be framed delicately, taking into account individual concerns while reinforcing the collective family legacy. Engaging a financial advisor as a neutral facilitator can also help guide these conversations, ensuring they remain focused on planning and preparation.
Additionally, families should be proactive in addressing any concerns about perceived favoritism or discrepancies in inheritance. Setting clear expectations around how wealth will be transferred and managed can promote transparency and reduce misunderstandings. Such foresight not only strengthens family bonds but also reinforces a culture of collaboration and empathy, paving the way for a smoother transition during wealth transfer.
The Role of Professional Advisors in Wealth Management
The complexity of wealth management necessitates engaging with various professional advisors who can provide strategic guidance and tailored advice. This may include estate planners, tax specialists, and financial advisors, all of whom play an integral role in enhancing the effectiveness of family wealth management strategies. Their expertise can help families navigate the intricacies of inheritance planning, wealth distribution, and tax implications, ensuring a seamless transition of assets.
Moreover, beneficiaries should not feel constrained to use the same advisors as their parents or grandparents. They have the autonomy to find professionals who resonate with their values and communication styles. Seeking these advisors can be empowering for heirs, as they can better understand their financial landscape and make informed decisions regarding their inheritance. Embracing this collaborative approach equips beneficiaries with the necessary tools to uphold their family legacies with confidence.
Creating a Comprehensive Estate Plan
A comprehensive estate plan is paramount for ensuring that wealth is transferred smoothly across generations. This plan outlines the distribution of assets and includes vital documents such as wills, trusts, and health care directives. By taking the time to craft a well-considered estate plan, families can reduce the likelihood of disputes and ensure that all members are aware of their roles and responsibilities regarding wealth management.
Additionally, estate planning should be viewed as an ongoing process rather than a one-time task. Regular reviews and updates of the estate plan can accommodate changing family dynamics and financial situations, ensuring that the plan remains relevant and effective. Engaging in discussions about these adjustments fosters transparency and prepares heirs to take on their roles as informed stewards of the family’s wealth.
The Psychological Impact of Inheritance on Beneficiaries
Inheriting wealth can evoke a range of psychological responses in beneficiaries, from feelings of responsibility to anxiety about managing newfound resources. It’s essential for families to acknowledge these emotional aspects and address them openly during the wealth transfer process. Encouraging conversations about the emotional implications of inheritance can help heirs prepare for the responsibilities they will assume and the potential pressures that may arise.
Moreover, supporting beneficiaries through the mental and emotional aspects of inheritance is crucial in fostering resilience. Whether it’s through family discussions, educational resources, or even engaging with financial psychologists, creating a supportive environment can empower heirs to embrace their roles with confidence. By addressing both financial literacy and psychological preparedness, families can enhance the overall effectiveness of the wealth transfer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is wealth transfer preparation and why is it important?
Wealth transfer preparation involves planning for the distribution of assets and wealth from one generation to the next. It is crucial because it ensures that heirs are ready to manage and preserve their inheritance responsibly, mitigating the risk of losing wealth over generations due to lack of preparation, poor communication, or mismanagement.
How does the Great Wealth Transfer impact inheritance planning?
The Great Wealth Transfer refers to the anticipated transfer of approximately $124 trillion from baby boomers to their heirs by 2048. This significant shift emphasizes the importance of effective inheritance planning, which includes educating heirs about financial literacy, family wealth management, and their responsibilities as beneficiaries.
What are the key components of financial literacy for heirs in the context of wealth transfer preparation?
Financial literacy for heirs includes understanding various wealth management strategies, the implications of taxes and trusts, and the responsibilities that come with managing an inheritance. This knowledge is essential for heirs to make informed decisions and to honor their benefactor’s wishes effectively.
How can families improve communication during the wealth transfer preparation process?
Improving communication involves openly discussing the family’s financial situation, inheritance plans, and the responsibilities of beneficiaries. Family meetings, guided by financial professionals or estate planners, can facilitate these discussions and help build trust and understanding among family members.
What roles do family wealth management and estate planning play in the Great Wealth Transfer?
Family wealth management and estate planning are critical in the Great Wealth Transfer as they involve creating strategies that not only prepare heirs to handle their inheritance but also ensure that the family’s wealth is preserved and effectively utilized over generations.
What are recipient responsibilities in wealth transfer preparation?
Recipient responsibilities in wealth transfer preparation include being proactive about understanding their inheritance, engaging in financial literacy education, and participating in family discussions about the values and intentions behind the wealth being transferred.
Are there resources available for heirs to learn about managing inherited wealth?
Yes, heirs can access various resources, including family offices, financial advisors, and educational programs focused on wealth management, taxation, and estate planning. These resources equip beneficiaries with the knowledge needed to manage their inheritance effectively.
What should families consider when creating a wealth transfer plan?
Families should consider their values, financial goals, the level of education and preparedness of heirs, and the potential tax implications of wealth transfer. This holistic view helps create a comprehensive plan that aligns with family wishes and supports a smooth transition of wealth.
How can procrastination affect wealth transfer preparation?
Procrastination can hinder effective wealth transfer preparation by delaying necessary conversations and planning, which can result in misunderstandings, family conflicts, or mismanagement of assets once the wealth is transferred. Starting discussions early can mitigate these risks.
What are some common mistakes in wealth transfer preparation?
Common mistakes include failing to communicate plans with heirs, neglecting to provide financial education, overlooking tax implications, and not updating estate plans regularly. Addressing these issues early can help ensure a smoother transfer process.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| The Great Wealth Transfer | Over $124 trillion is expected to be transferred to heirs by 2048. |
| Heirs’ Preparation | 70% of wealthy families lose their wealth by the second generation due to lack of preparation. |
| Communication Gaps | 60% of wealth transfer failures result from poor communication and trust issues within families. |
| Beneficiaries’ Concerns | Only 54% of heirs feel fully prepared to manage their inheritance responsibly. |
| Role of Advisors | Neutral third parties can facilitate discussions around wealth transfer planning. |
| Financial Literacy | Heirs must become financially literate and knowledgeable about wealth management to ensure responsible handling of assets. |
Summary
Wealth transfer preparation is essential for ensuring the successful transition of assets to the next generation. As massive wealth transfers are underway, it is crucial for both givers and receivers to engage in open communications and planning to mitigate risks such as mismanagement, taxes, and disputes. Families that prioritize education and dialogue about financial matters can help their heirs navigate the complexities of inherited wealth and ensure it serves as a lasting legacy.